Photoinduced Oxidation of Lipid Membranes in the Presence of the Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Ketoprofen
- PMID: 35323726
- PMCID: PMC8954693
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12030251
Photoinduced Oxidation of Lipid Membranes in the Presence of the Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Ketoprofen
Abstract
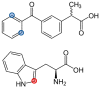
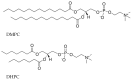
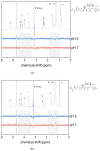
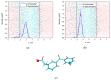
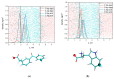
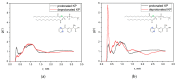
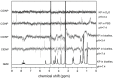
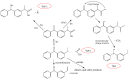
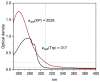
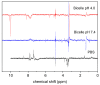
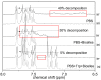
The damage of cell membranes induced by photosensitive drugs has attracted the significant attention of researchers in various fields of medicine. Ketoprofen (KP) is known to be the most photosensitive among the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The phototoxic side effects of KP and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are associated with the action of free radicals, but there is insufficient information about the nature of these radicals. In the present study, free radicals formed upon KP irradiation within lipid membranes were studied using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization (CIDNP) methods, as well as a molecular dynamics simulation. Our study confirmed the effective penetration of KP into the lipid bilayer and showed a significant effect of the nature of the medium on the photolysis mechanism. While, in a homogeneous solution, the main channel of KP photolysis is free radical-mediated monomolecular decomposition with formation of radical pairs of benzyl and CO2H● radicals, then, in the lipid membrane, the reaction route shifts towards the bimolecular reaction of KP photoreduction. In addition, the effect of the presence an electron donor (the amino acid tryptophan) on lipid oxidation has been studied. It was found that photoreaction of KP with tryptophan proceeds more efficiently than with lipid molecules.
Keywords: CIDNP; decarboxylation; free radicals; ketoprofen; lipid membranes; molecular dynamics; photosensitivity; phototoxicity; radical polymerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stereoselectivity of Interaction of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug S-Ketoprofen with L/D-Tryptophan in Phospholipid Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Apr 24;12(5):460. doi: 10.3390/membranes12050460. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629787 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of static magnetic fields on the photohemolysis of human erythrocytes by ketoprofen.Photochem Photobiol. 1998 May;67(5):591-5. Photochem Photobiol. 1998. PMID: 9613243
-
Photosensitivity to ketoprofen: mechanisms and pharmacoepidemiological data.Drug Saf. 2000 May;22(5):339-49. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200022050-00002. Drug Saf. 2000. PMID: 10830251 Review.
-
UVA-ketoprofen-induced hemoglobin radicals detected by immuno-spin trapping.Photochem Photobiol. 2003 Jun;77(6):585-91. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2003)077<0585:uhrdbi>2.0.co;2. Photochem Photobiol. 2003. PMID: 12870842
-
Ketoprofen 2.5% gel: a clinical overview.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011 Aug;15(8):943-9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21845805 Review.
Cited by
-
Metal Complexes of Omadine (N-Hydroxypyridine-2-thione): Differences of Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Behavior in Light and Dark Conditions with Possible Toxicity Implications.Molecules. 2023 May 20;28(10):4210. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104210. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241949 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction of Anthracycline Based Quinone-Chelators with Model Lipid Membranes: 1H NMR and MD Study.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;13(1):61. doi: 10.3390/membranes13010061. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676868 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselectivity of Interaction of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug S-Ketoprofen with L/D-Tryptophan in Phospholipid Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Apr 24;12(5):460. doi: 10.3390/membranes12050460. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629787 Free PMC article.
-
The phenomenon of phototoxicity and long-term risks of commonly prescribed and structurally diverse drugs.J Photochem Photobiol. 2024 Feb;19:100221. doi: 10.1016/j.jpap.2023.100221. Epub 2023 Dec 5. J Photochem Photobiol. 2024. PMID: 38389933 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

