Interaction of Human Serum Albumin with Uremic Toxins: The Need of New Strategies Aiming at Uremic Toxins Removal
- PMID: 35323736
- PMCID: PMC8953794
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12030261
Interaction of Human Serum Albumin with Uremic Toxins: The Need of New Strategies Aiming at Uremic Toxins Removal
Abstract
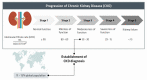
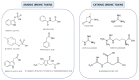
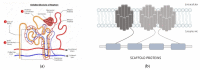
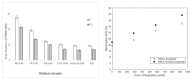
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is acknowledged worldwide to be a grave threat to public health, with the number of US end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients increasing steeply from 10,000 in 1973 to 703,243 in 2015. Protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUTs) are excreted by renal tubular secretion in healthy humans, but hardly removed by traditional haemodialysis (HD) in ESKD patients. The accumulation of these toxins is a major contributor to these sufferers' morbidity and mortality. As a result, some improvements to dialytic removal have been proposed, each with their own upsides and drawbacks. Longer dialysis sessions and hemodiafiltration, though, have not performed especially well, while larger dialyzers, coupled with a higher dialysate flow, proved to have some efficiency in indoxyl sulfate (IS) clearance, but with reduced impact on patients' quality of life. More efficient in removing PBUTs was fractionated plasma separation and adsorption, but the risk of occlusive thrombosis was worryingly high. A promising technique for the removal of PBUTs is binding competition, which holds great hopes for future HD. This short review starts by presenting the PBUTs chemistry with emphasis on the chemical interactions with the transport protein, human serum albumin (HSA). Recent membrane-based strategies targeting PBUTs removal are also presented, and their efficiency is discussed.
Keywords: OAT; OCT; chronic kidney disease (CKD); protein-bound uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;15(2):110. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020110. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUTs) in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients: Production pathway, challenges and recent advances in renal PBUTs clearance.NanoImpact. 2021 Jan;21:100299. doi: 10.1016/j.impact.2021.100299. Epub 2021 Jan 28. NanoImpact. 2021. PMID: 35559786 Review.
-
Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients Relate to Residual Kidney Function, Are Not Influenced by Convective Transport, and Do Not Relate to Outcome.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 7;12(4):234. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040234. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32272776 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improved dialytic removal of protein-bound uremic toxins by intravenous lipid emulsion in chronic kidney disease rats.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Nov 1;34(11):1842-1852. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfz079. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31071223
-
Ibuprofen-Immobilized Thin Films: A Novel Approach to Improve the Clearance of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Feb 7;16(5):6589-6604. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c15291. Epub 2024 Jan 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38282580
Cited by
-
Binding and detoxification efficiency of albumin decline after haemodialysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Jan 31;39(2):215-221. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad133. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 37558390 Free PMC article.
-
Portimine A maintains bioactivity following exposure to liver microsomes and cell lysates: no evidence for significant metabolic inactivation.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 23;42(7):278. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02826-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40549272
-
A Novel Strategy for Enhanced Sequestration of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Using Smart Hybrid Membranes.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Feb 28;14(3):138. doi: 10.3390/jfb14030138. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36976062 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Structural Homogeneity, Hydraulic Permeability, and Mechanical Performance of Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose Acetate/Silica Membranes: Spinodal Decomposition Mix.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;13(3):346. doi: 10.3390/membranes13030346. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984734 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;15(2):110. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020110. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- [(accessed on 1 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978141605185500002X.
-
- WHO Ageing-and-Health. [(accessed on 1 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
- Hsu C. Primer on kidney Diseases. NEJM Group; Boston, MA, USA: 2009. Clinical Evaluation of Kidney Function.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

