Study of Melamine-Formaldehyde/Phase Change Material Microcapsules for the Preparation of Polymer Films by Extrusion
- PMID: 35323742
- PMCID: PMC8950258
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12030266
Study of Melamine-Formaldehyde/Phase Change Material Microcapsules for the Preparation of Polymer Films by Extrusion
Abstract
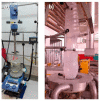
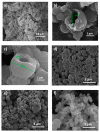
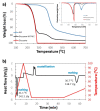
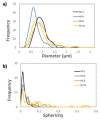
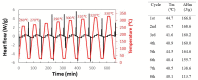
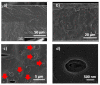
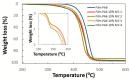
n-Eicosane-melamine formaldehyde microcapsules of an average size of 1.1 μm and latent heat of fusion of 146.2 ± 5.3 J/g have been prepared. They have been characterized by scanning electron microscopy, FTIR spectroscopy, calorimetric techniques, and thermogravimetric analyses. Under processing conditions, the microcapsules apparently preserved their properties, also maintaining their n-eicosane loading and heat storage capacity under washing conditions (water with detergent at 60 °C). The microcapsules synthesis has been scaled up for the fabrication of functional films by extrusion. For that, polymer films containing 10 wt.% of microcapsules were prepared at a pilot plant level. In those films, even though a fraction of the n-eicosane loading was lost during the extrusion process, the microcapsules showed good compatibility within the polyamide. The percentage of PCM in the polyamide 6 films was estimated by TGA, verifying also the heat storage capacity predicted by DSC (2.6 ± 0.7 J/g).
Keywords: heat storage; n-Eicosane-melamine formaldehyde microcapsules; phase change material; polyamide 6 films.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Valdes A., Ramos M., Beltran A., Garrigos M.C. Recent Trends in Microencapsulation for Smart and Active Innovative Textile Products. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018;22:1237–1248. doi: 10.2174/1385272822666180430130528. - DOI
-
- Algieri C., Chakraborty S., Pal U. Efficacy of phase inversion technique for polymeric membrane fabrication. J. Phase Chang. Mater. 2021;1 doi: 10.6084/jpcm.v1i1.10. - DOI
-
- Sherwin C., Bhat S., Hebbar S.P. Effect of plating time on surface morphology and coating thickness of nickel plating on copper surface. J. Phase Chang. Mater. 2021;1 doi: 10.6084/jpcm.v1i1.5. - DOI
-
- Paseta L., Antoran D., Coronas J., Tellez C. 110th Anniversary: Polyamide/Metal-Organic Framework Bilayered Thin Film Composite Membranes for the Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019;58:4222–4230. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b06017. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

