Final report on plasma ctDNA T790M monitoring during EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer (JP-CLEAR trial)
- PMID: 35323965
- PMCID: PMC9264253
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyac032
Final report on plasma ctDNA T790M monitoring during EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer (JP-CLEAR trial)
Erratum in
-
Correction.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov 3;52(11):1358. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyac156. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36124846 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
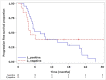
Osimertinib is active against T790M-positive epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer. We enrolled 122 sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients who were planned to receive or were receiving first-/second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors without disease progression and monitored plasma T790M every 1-2 months using the cobas® EGFR Mutation Test v2. We previously reported the concordance between T790M status in plasma and tissue. This is the final report on the sensitivity of plasma T790M and the efficacy of sequential osimertinib. The sensitivity was 21.1% (95% confidence interval: 6.1-45.6%). The best overall response was 25.0% (95% confidence interval: 9.8-46.7) in the plasma T790M-positive group and 28.6% (95% confidence interval: 8.4-58.1) in the plasma T790M-negative but tissue T790M-positive group. Median progression-free survival was 7.9 months (95% confidence interval: 4.7-17.5) for the former and 4.4 months (95% confidence interval: 3.0-N.E.) for the latter, with no statistically significant difference (P = 0.74).
Keywords: epidermal growth factor; liquid biopsy; lung neoplasm; mutation.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2380–8. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicenter, open-label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:141–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

