Thymine-starvation-induced chromosomal fragmentation is not required for thymineless death in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 35324030
- PMCID: PMC11574965
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14897
Thymine-starvation-induced chromosomal fragmentation is not required for thymineless death in Escherichia coli
Abstract
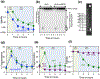
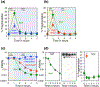
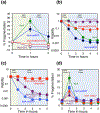
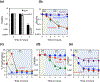
Thymine or thymidine starvation induces robust chromosomal fragmentation in Escherichia coli thyA deoCABD mutants and is proposed to be the cause of thymineless death (TLD). However, fragmentation kinetics challenges the idea that fragmentation causes TLD, by peaking before the onset of TLD and disappearing by the time TLD accelerates. Quantity and kinetics of fragmentation also stay unchanged in hyper-TLD-exhibiting recBCD mutant, making its faster and deeper TLD independent of fragmentation as well. Elimination of fragmentation without affecting cellular metabolism did not abolish TLD in the thyA mutant, but reduced early TLD in the thyA recBCD mutant, suggesting replication-dependent, but undetectable by pulsed-field gel, double-strand breaks contributed to TLD. Chromosomal fragmentation, but not TLD, was eliminated in both the thyA and thyA recBCD mutants harboring deoCABD operon. The expression of a single gene, deoA, encoding thymidine phosphorylase, was sufficient to abolish fragmentation, suggesting thymidine-to-thymine interconversion during T-starvation being a key factor. Overall, this study reveals that chromosomal fragmentation, a direct consequence of T-starvation, is either dispensable or redundant for the overall TLD pathology, including hyper-TLD in the recBCD mutant. Replication forks, unlike chromosomal fragmentation, may provide a minor contribution to TLD, but only in the repair-deficient thyA deoCABD recBCD mutant.
Keywords: deoCABD; recBCD; double-strand breaks; nucleotide salvage pathway; replication forks.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Thymineless Death in Escherichia coli Is Unaffected by Chromosomal Replication Complexity.J Bacteriol. 2019 Apr 9;201(9):e00797-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00797-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745374 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Damage Blocks Thymineless Death and Trimethoprim Poisoning in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2022 Jan 18;204(1):e0037021. doi: 10.1128/JB.00370-21. Epub 2021 Oct 11. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 34633866 Free PMC article.
-
Exopolysaccharide defects cause hyper-thymineless death in Escherichia coli via massive loss of chromosomal DNA and cell lysis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 29;117(52):33549-33560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012254117. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33318216 Free PMC article.
-
Thymine metabolism and thymineless death in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998;52:591-625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.52.1.591. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9891809 Review.
-
Thymineless Death Lives On: New Insights into a Classic Phenomenon.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015;69:247-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155749. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26253395 Review.
Cited by
-
Defects in the central metabolism prevent thymineless death in Escherichia coli, while still allowing significant protein synthesis.Genetics. 2024 Nov 6;228(3):iyae142. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae142. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 39212478 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Mediated Antibiotic Delivery to In Vivo Biofilm Infections: A Review.Chembiochem. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):e202400181. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400181. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38924307 Review.
-
UV induces codirectional replication-transcription conflicts and an alternative DnaA-dependent replication origin in the rnhAB mutants of Escherichiacoli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Apr 10;53(7):gkaf282. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf282. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40240002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad SI & Pritchard RH (1969) A map of four genes specifying enzymes involved in catabolism of nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in Escherichia coli. Molecular and General Genetics, 104, 351–359. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad SI, Kirk SH & Eisenstark A (1998) Thymine metabolism and thymineless death in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Annual Review of Microbiology, 52, 591–625. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann BJ (1987) Derivations and genotypes of some mutant derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular Biology (Neidhardt FC, Ed), pp 1190–1219, ASM Press, Washington D. C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

