Echinococcus multilocularis drives the polarization of macrophages by regulating the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway and thus affects liver fibrosis
- PMID: 35324411
- PMCID: PMC9161885
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2056690
Echinococcus multilocularis drives the polarization of macrophages by regulating the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway and thus affects liver fibrosis
Abstract
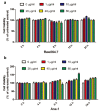
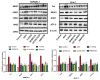
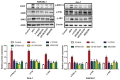
Echinococcus multilocularis is a small parasite that causes alveolar echinococcosis. It primarily induces liver disorder, such as liver fibrosis and even liver cancer, which severely endangers human lives. This study aims to explore the efficacy of Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen in preventing and alleviating alveolar echinococcosis-induced liver fibrosis and determine the underlying mechanism. We first identified the optimal dose and time of Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen. The protein levels of key genes in the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway were remarkably upregulated in RAW264.7 and Ana-1 cells induced with 80 μg/mL Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen for 8 h. Interestingly, the upregulated expression levels were remarkably reversed by the RhoA, JNK, ERK, or p38 inhibitor, confirming the significance of the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway. In addition, the relative contents of M2 polarization markers IL-10 and Arg-1 in macrophages induced with 80 μg/mL Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen for 8 h increased, whereas those of M1 polarization markers IL-12 and NOS-2 decreased. Mouse hepatic stellate cells were the key components of the hepatocellular carcinoma tumor microenvironment. Hepatic stellate cells were activated by Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen and transformed into the morphology of myofibroblasts in response to liver disorders. By detecting the marker of myofibroblast formation, RhoA inhibitor remarkably reduced the positive expression of α-SMA in mouse hepatic stellate cells induced with Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen. Therefore, Echinococcus multilocularis soluble antigen remarkably activated the RhoA-MAPK pathways in macrophages, further inducing the polarization of macrophages and ultimately causing liver fibrosis.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that infection with Echinococcus multilocularis activates the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway and subsequently induces macrophage polarization to promote hepatic stellate cells activation leading to liver fibrosis.
Aims: To investigate the mechanism by which soluble antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis affects liver fibrosis through the RhoA-MAPK pathway driving polarization of macrophages.
Goals: To identify new pathways of intervention and drug targets for the regulation of macrophage polarity phenotype switching and the attenuation or inhibition of the development and treatment of liver fibrosis caused by Echinococcus multilocularis infection.
Keywords: Echinococcus multilocularis; RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway; liver fibrosis; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
