Targeting Forkhead box O1-aquaporin 5 axis mitigates neuropathic pain in a CCI rat model through inhibiting astrocytic and microglial activation
- PMID: 35324416
- PMCID: PMC9161847
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2053032
Targeting Forkhead box O1-aquaporin 5 axis mitigates neuropathic pain in a CCI rat model through inhibiting astrocytic and microglial activation
Abstract
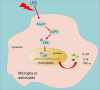
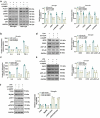
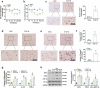
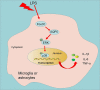
Forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) is a critical molecule in modulating cell growth, differentiation and metabolism, acting as a vital transcription factor. This study explored the role of FoxO1 in chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain (NP). Microglial and astrocyte activation was achieved with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/mL) to establish an in-vitro NP model. Morphological alterations in LPS-induced microglia and astrocytes were assayed by light microscopy. The levels of inflammatory cytokines and proteins in microglia and astrocytes were gauged by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and Western blot (WB). The CCI-induced NP rat model was constructed for investigating the FoxO1-AQP5 axis in NP. LPS markedly expanded the expression of inflammatory factors and boosted the expression of FoxO1 and AQP5 in microglia and astrocytes. Inhibition of FoxO1 or AQP5 dramatically decreased the LPS-induced inflammation in microglia and astrocytes. In vivo, CCI exacerbated the inflammatory response and NP symptoms and substantially raised the contents of FoxO1 and AQP5 in rats' spinal cord tissues. Intrathecal administration of the Sirt1 agonist Resveratrol abated CCI-induced activation of FoxO1 and AQP5, abrogated CCI-induced mechanical hyperalgesia and thermal hyperalgesia, depressed microglial and astrocyte activation, and declined the generation of pro-inflammatory mediators in spinal cord tissues. Mechanistically, blocking the FoxO1-AQP5 pathway inactivated the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Suppressing the FoxO1-AQP5 axis alleviated CCI-induced NP and inflammatory responses by modulating the ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: AQP5; FoxO1; chronic constriction injury; inflammation; neuropathic pain; pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Montelukast attenuates neuropathic pain through inhibiting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B in a rat model of chronic constriction injury.Anesth Analg. 2014 May;118(5):1090-6. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000174. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24686047
-
Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in spinal microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 May 11;17(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1731-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32393298 Free PMC article.
-
Levo-corydalmine attenuates microglia activation and neuropathic pain by suppressing ASK1-p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in rat spinal cord.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2020 Mar;45(3):219-229. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100875. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 31898581
-
Pulsed Radiofrequency on Dorsal Root Ganglion Relieved Neuropathic Pain Associated with Downregulation of the Spinal Interferon Regulatory Factor 8, Microglia, p38MAPK Expression in a CCI Rat Model.Pain Physician. 2018 Jul;21(4):E307-E322. Pain Physician. 2018. PMID: 30045596
-
Neuropathic Pain: Biomolecular Intervention and Imaging via Targeting Microglia Activation.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 10;11(9):1343. doi: 10.3390/biom11091343. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocyte senescence-like response related to peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Aug 15;28(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00474-5. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37582709 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Axon Guidance by Slit2 and Netrin-1 Signaling in the Lacrimal Gland of Aqp5 Knockout Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Sep 1;64(12):27. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.12.27. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37707834 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for studying mammalian aquaporin biology.Biol Methods Protoc. 2023 Nov 11;8(1):bpad031. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpad031. eCollection 2023. Biol Methods Protoc. 2023. PMID: 38046463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal astrocytes involved in the pathogenesis and treatment of neuropathic pain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Feb 21;19:1547524. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1547524. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40062207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-5 Dynamic Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1889. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031889. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
