Insulin-like growth factor role in determining the anti-cancer effect of metformin: RCT in prostate cancer patients
- PMID: 35324467
- PMCID: PMC9066575
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-21-0375
Insulin-like growth factor role in determining the anti-cancer effect of metformin: RCT in prostate cancer patients
Abstract
Objective: Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), a principal therapy in patients with prostate cancer, is associated with the development of obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperinsulinemia. Recent evidence indicates that metformin may slow cancer progression and improves survival in prostate cancer patients, but the mechanism is not well understood. Circulating insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are bound to high-affinity binding proteins, which not only modulate the bioavailability and signalling of IGFs but also have independent actions on cell growth and survival. The aim of this study was to investigate whether metformin modulates IGFs, IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), and the pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) - stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) axis.
Design and methods: In a blinded, randomised, cross-over design, 15 patients with prostate cancer on stable ADT received metformin and placebo treatment for 6 weeks each. Glucose metabolism along with circulating IGFs and IGFBPs was assessed.
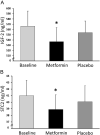
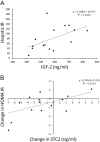
Results: Metformin significantly reduced the homeostasis model assessment as an index of insulin resistance (HOMA IR) and hepatic insulin resistance. Metformin also reduced circulating IGF-2 (P < 0.05) and IGFBP-3 (P < 0.01) but increased IGF bioactivity (P < 0.05). At baseline, IGF-2 correlated significantly with the hepatic insulin resistance (r2= 0.28, P < 0.05). PAPP-A remained unchanged but STC2 declined significantly (P < 0.05) following metformin administration. During metformin treatment, change in HOMA IR correlated with the change in STC2 (r2= 0.35, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Metformin administration alters many components of the circulating IGF system, either directly or indirectly via improved insulin sensitivity. Reduction in IGF-2 and STC2 may provide a novel mechanism for a potential metformin-induced antineoplastic effect.
Keywords: IGFBP-3; bioactive IGF-1; insulin resistance; pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A; stanniocalcin 2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic improvement after gastric bypass correlates with changes in IGF-regulatory proteins stanniocalcin-2 and IGFBP-4.Metabolism. 2021 Nov;124:154886. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154886. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Metabolism. 2021. PMID: 34506805
-
The IGF system in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with prednisolone or infliximab: potential role of the stanniocalcin-2 / PAPP-A / IGFBP-4 axis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun 3;19(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-1000-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31159802 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy-associated plasma proteins and Stanniocalcin-2 - Novel players controlling IGF-I physiology.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2020 Aug-Oct;53-54:101330. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2020.101330. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2020. PMID: 32693362 Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein production in bovine retinal endothelial cells.Metabolism. 1997 Dec;46(12):1367-79. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90134-7. Metabolism. 1997. PMID: 9439529
-
[Molecular action of insulin-sensitizing agents].Endokrynol Pol. 2005 May-Jun;56(3):308-13. Endokrynol Pol. 2005. PMID: 16350724 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The development and benefits of metformin in various diseases.Front Med. 2023 Jun;17(3):388-431. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-0998-6. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 37402952 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Prostate Cancer Cells Survival and Their Therapeutic Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2939. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032939. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heritability and circulating concentrations of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A and stanniocalcin-2 in elderly monozygotic and dizygotic twins.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 2;14:1193742. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1193742. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37334305 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Insulin, Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1, Testosterone and Lipid Profile Levels in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer at Diagnosis.Cureus. 2024 Dec 8;16(12):e75342. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75342. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39781138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lam T, Birzniece V, McLean M, Gurney H, Hayden A, Cheema BS. The adverse effects of androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer and the benefits and potential anti-oncogenic mechanisms of progressive resistance training. Sports Medicine: Open 20206 13. (10.1186/s40798-020-0242-8) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Derweesh IH, Diblasio CJ, Kincade MC, Malcolm JB, Lamar KD, Patterson AL, Kitabchi AE, Wake RW. Risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus and worsening glycaemic variables for established diabetes in men undergoing androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. BJU International 20071001060–1065. (10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07184.x) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

