Saporin as a Commercial Reagent: Its Uses and Unexpected Impacts in the Biological Sciences-Tools from the Plant Kingdom
- PMID: 35324681
- PMCID: PMC8952126
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14030184
Saporin as a Commercial Reagent: Its Uses and Unexpected Impacts in the Biological Sciences-Tools from the Plant Kingdom
Abstract
Saporin is a ribosome-inactivating protein that can cause inhibition of protein synthesis and causes cell death when delivered inside a cell. Development of commercial Saporin results in a technology termed 'molecular surgery', with Saporin as the scalpel. Its low toxicity (it has no efficient method of cell entry) and sturdy structure make Saporin a safe and simple molecule for many purposes. The most popular applications use experimental molecules that deliver Saporin via an add-on targeting molecule. These add-ons come in several forms: peptides, protein ligands, antibodies, even DNA fragments that mimic cell-binding ligands. Cells that do not express the targeted cell surface marker will not be affected. This review will highlight some newer efforts and discuss significant and unexpected impacts on science that molecular surgery has yielded over the last almost four decades. There are remarkable changes in fields such as the Neurosciences with models for Alzheimer's Disease and epilepsy, and game-changing effects in the study of pain and itch. Many other uses are also discussed to record the wide-reaching impact of Saporin in research and drug development.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; Alzheimer’s disease; RIP; Saporin; animal model; cancer; immunotoxins; internalization; lesion; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of or affiliated with Advanced Targeting Systems. The information provided in this article is based on independent publications from scientists who use saporin conjugates. Author D.H. owns stocks in Advanced Targeting Systems.
Figures
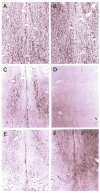
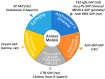
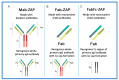
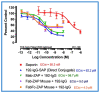
Similar articles
-
Streptavidin-Saporin: Converting Biotinylated Materials into Targeted Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;15(3):181. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030181. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saporin, a ribosome-inactivating protein used to prepare immunotoxins, induces cell death via apoptosis.Br J Haematol. 1996 Jun;93(4):789-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.d01-1730.x. Br J Haematol. 1996. PMID: 8703804
-
Comparison of the performance of anti-CD7 and anti-CD38 bispecific antibodies and immunotoxins for the delivery of saporin to a human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line.Hematol Oncol. 1995 Jul-Aug;13(4):185-200. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900130403. Hematol Oncol. 1995. PMID: 7557895
-
Targeting of saporin to Hodgkin's lymphoma cells by anti-CD30 and anti-CD25 bispecific antibodies.Br J Haematol. 1998 Sep;102(4):1061-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00859.x. Br J Haematol. 1998. PMID: 9734659
-
Neuronal lesioning with axonally transported toxins.J Neurosci Methods. 2000 Nov 15;103(1):73-82. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00297-1. J Neurosci Methods. 2000. PMID: 11074097 Review.
Cited by
-
Streptavidin-Saporin: Converting Biotinylated Materials into Targeted Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;15(3):181. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030181. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of arcuate nucleus kisspeptin and Kiss1R in regulation of the ovine luteinizing hormone surge.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 May;37(5):e70010. doi: 10.1111/jne.70010. Epub 2025 Mar 3. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40033679
-
Quantum Dot-Based Screening Identifies F3 Peptide and Reveals Cell Surface Nucleolin as a Therapeutic Target for Rhabdomyosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;14(20):5048. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205048. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291832 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking saponin biosynthesis in soapwort.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Feb;21(2):215-226. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01681-7. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39043959 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Protein Delivery: Approaches, Challenges, and Clinical Applications.BME Front. 2024 Jan 25;5:0035. doi: 10.34133/bmef.0035. eCollection 2024. BME Front. 2024. PMID: 38282957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourrie B.J.P., Casellas P., Blythman H.E., Jansen F.K. Study of the plasma clearance of antibody–ricin-A-chain immunotoxins. Evidence for specific recognition sites on the A chain that mediate rapid clearance of the immunotoxin. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1986;155:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09451.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

