The Serum Level of IL-31 in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus: What Can We Expect?
- PMID: 35324695
- PMCID: PMC8955714
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14030197
The Serum Level of IL-31 in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus: What Can We Expect?
Abstract
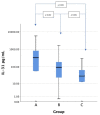
Chronic-kidney-disease-associated pruritus (CKD-aP) is one of the most common and burdensome dermatological symptoms affecting patients undergoing dialysis, and its etiopathogenesis has still not been fully discovered. This study was designed to investigate the possible contribution of interleukin-31 (IL-31) to the pathogenesis of itch in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (HD). We evaluated the serum level of IL-31 in HD patients with pruritus, in HD patients without pruritus and in healthy controls, as well as its correlation to the severity of itch. The study enrolled 175 adult subjects. The participants were divided into three groups. Group A included 64 patients on maintenance HD with CKD-aP, Group B included 62 patients on maintenance HD not reporting CKD-aP and Group C included 49 healthy controls. Pruritus severity was assessed using the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), and the serum levels of IL-31 were measured. The results showed that the IL-31 serum level was significantly higher in the itchy group (p < 0.001) in comparison to the patients free from pruritus. Moreover, a marginal trend towards significance (r = 0.242, p = 0.058) was observed between the IL-31 serum level and itch intensity. Our study supports earlier findings on the extended role of IL-31 in the development of CKD-aP.
Keywords: chronic-kidney-disease-associated pruritus; hemodialysis patients; interleukin-31; renal failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated interleukin 31 serum levels in hemodialysis patients are associated with uremic pruritus.Cytokine. 2021 Feb;138:155369. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155369. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33221158
-
Difelikefalin improves itch-related sleep disruption in patients undergoing haemodialysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Jun 28;39(7):1125-1137. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad245. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 37968132 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of Baseline Itch Severity on Treatment Outcomes With Difelikefalin in Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Pruritus Receiving Maintenance Haemodialysis: An Exploratory Analysis.J Ren Care. 2025 Jun;51(2):e70017. doi: 10.1111/jorc.70017. J Ren Care. 2025. PMID: 40327387 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Difelikefalin: A New κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Hemodialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus.Ann Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;57(4):480-488. doi: 10.1177/10600280221115889. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Ann Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 35942600 Review.
-
The factors that are associated with itching in chronic kidney patients and evaluation of itching with the 5d itch scale.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Jun;56(6):1973-1981. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03937-y. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38334911 Review.
Cited by
-
High Serum IL-31 Concentration Is Associated with Itch among Renal Transplant Recipients.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 25;11(15):4309. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154309. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35893400 Free PMC article.
-
Blockage of the IL-31 Pathway as a Potential Target Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 8;15(2):577. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020577. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus from 2004 to 2023.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 30;104(22):e42628. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042628. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40441218 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of S100A6 Protein with the Four-Helical Cytokines.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 4;13(9):1345. doi: 10.3390/biom13091345. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759746 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of renal pruritus with dupilumab monotherapy: A case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2024 Jun 10;12:2050313X241260491. doi: 10.1177/2050313X241260491. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38864030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pisoni R.L., Wikström B., Elder S.J., Akizawa T., Asano Y., Keen M.L., Saran R., Mendelssohn D.C., Young E.W., Port F.K. Pruritus in haemodialysis patients: International results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006;21:3495–3505. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl461. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

