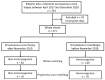
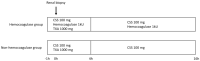
Effect of Hemocoagulase on the Prevention of Bleeding after Percutaneous Renal Biopsy
- PMID: 35324720
- PMCID: PMC8951486
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14030223
Effect of Hemocoagulase on the Prevention of Bleeding after Percutaneous Renal Biopsy
Abstract
A percutaneous renal biopsy is an essential tool for the diagnosis of various renal diseases; however, post-biopsy bleeding is a major complication. Hemocoagulase is a detoxified and purified snake venom enzyme that is widely used to prevent post-procedural bleeding. In this study, we retrospectively analyzed the effect of hemocoagulase on post-renal biopsy bleeding. We included 221 patients who underwent percutaneous renal biopsy between April 2017 and December 2020 and analyzed post-renal biopsy hemoglobin (Hb) decline in patients who were administered a periprocedural hemocoagulase injection. After the renal biopsy, the mean Hb decrease in the entire patient cohort was 0.33 ± 0.84 g/dL. Periprocedural hemocoagulase injection lowered the Hb decline post-renal biopsy (0.50 ± 0.87 vs. 0.23 ± 0.80 g/dL, p = 0.0204). The propensity-matched cohort was also adjusted for factors influencing postprocedural bleeding; periprocedural hemocoagulase injection reduced the Hb decline post-renal biopsy (0.56 ± 0.89 vs. 0.17 ± 0.74 g/dL, p = 0.006). There were no adverse events (e.g., thrombosis and anaphylactic shock) due to hemocoagulase. Our study demonstrated the beneficial effect of hemocoagulase on post-renal biopsy Hb decline, suggesting its clinical value in preventing post-renal biopsy bleeding.
Keywords: complication; hemocoagulase; post-procedural bleeding; renal biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paradoxical pulmonary hemorrhage associated with hemocoagulase batroxobin in a patient with hemoptysis: A CARE-compliant case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jan 29;100(4):e24040. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024040. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33530198 Free PMC article.
-
Hemocoagulase reduces postoperative bleeding and blood transfusion in cardiac surgical patients: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(52):e18534. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018534. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31876750 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of hemocoagulase for improvement of coagulation and reduction of bleeding in fracture-related hip hemiarthroplasty geriatric patients: A prospective, single-blinded, randomized, controlled study.Injury. 2017 Apr;48(4):914-919. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.11.028. Epub 2016 Nov 27. Injury. 2017. PMID: 28238301 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypofibrinogenemia Caused by Hemocoagulase After Colon Polyps Excision.Am J Case Rep. 2017 Mar 22;18:291-293. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.902059. Am J Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28325889 Free PMC article.
-
Hemocoagulase agkistrodon-induced anaphylactic shock: A case report and literature review.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Feb;54(2):129-34. doi: 10.5414/CP202296. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26636421 Review.
Cited by
-
Perioperative blood loss of sequential administration of hemocoagulase Agkistrodon and Tranexamic acid for primary total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 May 13;20(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05867-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40355919 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Validation and modification of existing bleeding complications prediction models for percutaneous renal biopsy: a prospective study.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 18;12:e18741. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18741. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39713131 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with Glomerular Yield in Percutaneous Kidney Biopsy.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 6;12(12):3877. doi: 10.3390/jcm12123877. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373572 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the risk factors of hemagglutinase-associated hypofibrinogenemia can improve the prognosis of patients.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Jun 27;17(6):101206. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.101206. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40584489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pombas B., Rodríguez E., Sánchez J., Radosevic A., Gimeno J., Busto M., Barrios C., Sans L., Pascual J., Soler M.J. Risk Factors Associated with Major Complications After Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Renal Biopsy of Native Kidneys. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2020;45:122–130. doi: 10.1159/000504544. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ubara Y., Kawaguchi T., Nagasawa T., Miura K., Katsuno T., Morikawa T., Ishikawa E., Ogura M., Matsumura H., Kurayama R., et al. Committee of Practical Guide for Kidney Kidney biopsy guidebook 2020 in Japan. Kidney biopsy guidebook 2020 in Japan. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021;25:325–364. doi: 10.1007/s10157-020-01986-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous