In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Flumethrin Pyrethroid on SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells: Apoptosis Associated with Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 35324756
- PMCID: PMC8955675
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10030131
In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Flumethrin Pyrethroid on SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells: Apoptosis Associated with Oxidative Stress
Abstract
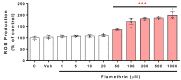
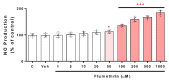
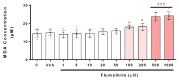
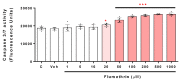
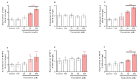
Pyrethroids are neurotoxicants for animals, showing a pattern of toxic action on the nervous system. Flumethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid, is used against ectoparasites in domestic animals, plants, and for public health. This compound has been shown to be highly toxic to bees, while its effects on other animals have been less investigated. However, in vitro studies to evaluate cytotoxicity are scarce, and the mechanisms associated with this effect at the molecular level are still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the oxidative stress and cell death induction in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in response to flumethrin exposure (1-1000 µM). Flumethrin induced a significant cytotoxic effect, as evaluated by MTT and LDH leakage assays, and produced an increase in the biomarkers of oxidative stress as reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide (ROS and NO) generation, malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration, and caspase-3 activity. In addition, flumethrin significantly increased apoptosis-related gene expressions (Bax, Casp-3, BNIP3, APAF1, and AKT1) and oxidative stress and antioxidative (NFκB and SOD2) mediators. The results demonstrated, by biochemical and gene expression assays, that flumethrin induces oxidative stress and apoptosis, which could cause DNA damage. Detailed knowledge obtained about these molecular changes could provide the basis for elucidating the molecular mechanisms of flumethrin-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: SH-SY5Y cells; apoptosis; flumethrin; neurotoxicity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest between the authors.
Figures

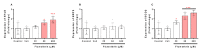
Similar articles
-
Ipconazole Induces Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Proinflammation in SH-SY5Y Cells.Toxics. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):566. doi: 10.3390/toxics11070566. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37505534 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and related gene expression effects of cyfluthrin in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: Protective effect of melatonin.Environ Res. 2019 Oct;177:108579. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108579. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Environ Res. 2019. PMID: 31330490
-
Use of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells to evaluate glyphosate-induced effects on oxidative stress, neuronal development and cell death signaling pathways.Environ Int. 2020 Feb;135:105414. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105414. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 31874349
-
Oxidative stress and gene expression profiling of cell death pathways in alpha-cypermethrin-treated SH-SY5Y cells.Arch Toxicol. 2017 May;91(5):2151-2164. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1864-y. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27704156
-
Effect of Acrylamide and Mycotoxins in SH-SY5Y Cells: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;16(2):87. doi: 10.3390/toxins16020087. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38393165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implication of Pyrethroid Neurotoxicity for Human Health: A Lesson from Animal Models.Neurotox Res. 2024 Dec 16;43(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s12640-024-00723-1. Neurotox Res. 2024. PMID: 39680194 Review.
-
3-Phenoxybenzoic Acid Induces Neuronal Pentraxin 2 to Upregulate Complement Activity and Promotes Microglia-Mediated Neuronal Synaptic Damage.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jun 26;75(3):83. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02374-z. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40571817
-
Oxidative and Molecular-Structural Alterations of Spermatozoa in Swine and Ram Exposed to the Triazole Ipconazole.Toxics. 2025 Feb 28;13(3):176. doi: 10.3390/toxics13030176. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40137503 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Involvement of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Proinflammation in Ipconazole-Induced Cytotoxicity in Human Endothelial-like Cells.Toxics. 2023 Oct 5;11(10):839. doi: 10.3390/toxics11100839. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37888690 Free PMC article.
-
Ipconazole Induces Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Proinflammation in SH-SY5Y Cells.Toxics. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):566. doi: 10.3390/toxics11070566. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37505534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao L.N. Master’s Thesis. Shanghai Ocean University; Shanghai, China: 2014. Residue and Risk Assessment of 7 Kinds of Pyrethroids in Water Environment in the Pearl River Delta.
-
- Thatheyus A., Selvam A.D.G. Synthetic Pyrethroids: Toxicity and Biodegradation. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013;1:33–36. doi: 10.12691/aees-1-3-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

