Disinfection Procedures and Their Effect on the Microorganism Colonization of Dental Impression Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 35324812
- PMCID: PMC8945053
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9030123
Disinfection Procedures and Their Effect on the Microorganism Colonization of Dental Impression Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
Abstract
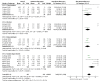
Dental impressions are contaminated with potentially pathogenic microorganisms when they come into contact with patient blood, saliva, and plaque. Numerous disinfectants are used; however, no sole disinfectant can be designated as universal for all the impression materials. Thus, the aim of this study is to systemically review the literature to evaluate the effect of the existing disinfection procedures on the bacterial colonization of dental impression materials. This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted according to the PRISMA statement. PubMed (MEDLINE), Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE, and SciELO databases were screened up to April 2021. Eligibility criteria included in vitro studies reporting the antibacterial activity of disinfectant solutions in dental impression materials. The meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager (version 5.3.5). A global comparison was performed with the standardized mean difference based on random-effect models at a significance level of α = 0.05. A total of seven studies were included in the meta-analysis. The included studies described the effect of disinfection processes with chlorhexidine gluconate, alcohol, sodium hypochlorite, glutaraldehyde, and hydrogen peroxide in alginate, polyvinyl siloxane, and polyether impression materials. The meta-analyses showed that the use of chlorhexidine, alcohol, glutaraldehyde, and sodium hypochlorite reduced the colony-forming units by a milliliter (CFU/mL) in alginate (p < 0.001). On the other hand, glutaraldehyde, sodium hypochlorite, and alcohol reduced the CFU/mL in polyvinyl siloxane (p < 0.001). Finally, alcohol and glutaraldehyde reduced the CFU/mL in polyether material (p < 0.001). High heterogenicity was observed for the alginate and polyvinyl siloxane materials (I2 = 74%; I2 = 90%). Based on these in vitro studies, the disinfection of impression materials with several disinfection agents reduces the CFU/mL count.
Keywords: antibacterial effect; dental impressions; disinfectant agents; disinfection; oral bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of chemical disinfection on the dimensional stability of polyvinyl ether siloxane impression material: a systemic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jul 10;23(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03168-8. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37430254 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Effect of Chemical Disinfectants and Ultraviolet Disinfection on Dimensional Stability of the Polyvinyl Siloxane Impressions.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019 Mar-Apr;9(2):152-158. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_406_18. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019. PMID: 31058065 Free PMC article.
-
Disinfection efficacy of sodium hypochlorite and glutaraldehyde and their effects on the dimensional stability and surface properties of dental impressions: a systematic review.PeerJ. 2023 Feb 20;11:e14868. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14868. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36846444 Free PMC article.
-
Effects chemical disinfectants on surface roughness of conventional impression materials used for dental prosthetic procedures.Niger J Clin Pract. 2022 Sep;25(9):1484-1489. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_1920_21. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36149208
-
Antimicrobial effect of 4 disinfectants on alginate, polyether, and polyvinyl siloxane impression materials.Int J Prosthodont. 2007 May-Jun;20(3):299-307. Int J Prosthodont. 2007. PMID: 17580464
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Efficacy of Chitosan Nanoparticles in Irreversible Hydrocolloid Impression Materials: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Feb 3;17(2):e78414. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78414. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40046398 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Efficiency of Hypochlorous Acid and Its Effect on Some Properties of Alginate Impression Material.Int J Dent. 2023 Nov 14;2023:8584875. doi: 10.1155/2023/8584875. eCollection 2023. Int J Dent. 2023. PMID: 38021346 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Disinfection Protocols for Dental Impressions in Prosthodontics.Cureus. 2024 Jul 27;16(7):e65535. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65535. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39188490 Free PMC article.
-
Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study.Materials (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;17(17):4221. doi: 10.3390/ma17174221. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39274611 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Recent Advances in Biomaterials and Dental Disease" Part I.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 1;10(1):55. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10010055. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jennings K.J., Samaranayake L.P. The Persistence of Microorganisms on Impression Materials Following Disinfection. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1991;4:382–387. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

