Electromagnetic Force-Driven Needle-Free in Ovo Injection Device
- PMID: 35324876
- PMCID: PMC8951732
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9030147
Electromagnetic Force-Driven Needle-Free in Ovo Injection Device
Abstract
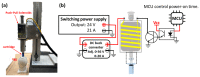
Needle-free injections are mainly used for administering human or mammalian vaccines or drugs. However, poultry vaccines, in ovo injections to embryos, subcutaneous injections to chickens, and intramuscular injections are administered using needle injections. This article presents a new needle-free in ovo injection device method that uses push-pull solenoids to eject liquid jets, mainly for embryonic eggs of chickens. Furthermore, our study investigated the suitable jet pressures for using this method and the post-injection hatching rates in 18-day-old embryonic eggs. Using this method, we could deliver the liquid to the allantoic and amniotic cavities or the muscle tissue through the egg membrane of the air chamber using a jet pressure of ~6-7 MPa or ~8 MPa. After injecting 0.25 mL of 0.9% saline into 18-day-old Lohmann breed layer embryonic eggs and specific pathogen-free (SPF) embryonic eggs at a jet pressure of ~7 MPa, we observed hatching rates of 98.3% and 85.7%, respectively. This study's electromagnetic needle-free in ovo injection device can apply vaccine or nutrient solution injection for embryo eggs and serve as a reference for future studies on needle-free in ovo injection automation systems, jet pressure control, and injection pretreatment processes.
Keywords: embryonic egg; in ovo; injection device; needle-free.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optimum site for in ovo amino acid injection in broiler breeder eggs.Poult Sci. 2001 Oct;80(10):1425-9. doi: 10.1093/ps/80.10.1425. Poult Sci. 2001. PMID: 11599700
-
Influence of in ovo arginine feeding on hatching traits and post-hatch performance of FUNAAB-Alpha chickens in two housing types.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2020 Sep;52(5):2349-2357. doi: 10.1007/s11250-020-02258-x. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2020. PMID: 32166502
-
Embryo growth and amino acid concentration profiles of broiler breeder eggs, embryos, and chicks after in ovo administration of amino acids.Poult Sci. 2001 Oct;80(10):1430-6. doi: 10.1093/ps/80.10.1430. Poult Sci. 2001. PMID: 11599701
-
Jet injection devices for the needle-free administration of compounds, vaccines, and other agents.Int J Pharm Compd. 2013 Jul-Aug;17(4):270-80. Int J Pharm Compd. 2013. PMID: 24261141 Review.
-
Bibliographical Mapping of Research into the Relationship between In Ovo Injection Practice and Hatchability in Poultry.Vet Sci. 2023 Apr 17;10(4):296. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10040296. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37104451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang J., Cai K., Mishra R., Jha R. In ovo supplementation of chitooligosaccharide and chlorella polysaccharide affects cecal microbial community, metabolic pathways, and fermentation metabolites in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020;99:4776–4785. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.06.061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peebles E.D., Barbosa T.M., Cummings T.S., Dickson J., Womack S.K. Comparative effects of in ovo versus subcutaneous administration of the Marek’s disease vaccine and pre-placement holding time on the early post-hatch quality of Ross × Ross 708 broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2016;95:2038–2044. doi: 10.3382/ps/pew132. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boone A.C., Käser T., Cortes A.L., Kulkarni R.R., López de Juan Abad B.A., Villalobos T., Esandi J., Perozo F., Lemiere S., Gimeno I.M. In ovo vaccination with herpesvirus of turkey enhances innate and cellular responses in meat-type chickens: Effect of vaccine dose and strain. Vaccine. 2020;38:4837–4845. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.050. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

