Real-life quantitative G6PD screening in Plasmodium vivax patients in the Brazilian Amazon: A cost-effectiveness analysis
- PMID: 35324892
- PMCID: PMC8982881
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010325
Real-life quantitative G6PD screening in Plasmodium vivax patients in the Brazilian Amazon: A cost-effectiveness analysis
Abstract
Background: As quantitative glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDd) screening tools are evaluated in operational studies, questions remain as to whether they are cost-effective. Here, a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed to estimate the Incremental Cost-effectiveness Ratio (ICER) of the introduction of quantitative screening test to detect G6PDd among P. vivax carriers in two municipalities in the Brazilian Amazon.
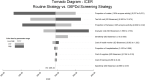
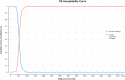
Methodology/principal findings: This cost-effectiveness analysis evaluated the use of the Standard G6PD quantitative screening test in vivax malaria treatment units in two municipalities of the Brazilian Amazon. Using the perspective of the Brazilian public health system, the analysis was performed for the outcome 'PQ-associated hospitalization avoided', based on a decision tree model. The results indicated that the G6PDd screening strategy compared with the routine strategy was highly cost-effective, with an ICER of US$495 per additional hospitalization avoided, which represented less than 8% of one Brazilian gross domestic product per capita (US$6,822). The uncertainties evaluated in the sensitivity analysis did not significantly affect the ICER identified in the base-case.
Conclusions/significance: This cost-effectiveness analysis showed the quantitative G6PD testing was effective in avoiding PQ-associated hospitalizations. The incorporation of G6PD screening is of paramount importance towards P. vivax malaria elimination in the Amazon to promote the safe use of primaquine and tafenoquine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of rapid diagnostic tests for G6PD deficiency in patients with Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Brazilian Amazon.Malar J. 2016 Feb 11;15:82. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1140-x. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 26864333 Free PMC article.
-
G6PD deficiency in male individuals infected by Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Brazilian Amazon: a cost study.Malar J. 2015 Mar 24;14:126. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0647-x. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 25889063 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of G6PD diagnostic test for Plasmodium vivax radical cure in Lao PDR: An economic modelling study.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 25;17(4):e0267193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267193. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35468145 Free PMC article.
-
Primaquine treatment and relapse in Plasmodium vivax malaria.Pathog Glob Health. 2016;110(1):1-8. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2015.1133033. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27077309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges for achieving safe and effective radical cure of Plasmodium vivax: a round table discussion of the APMEN Vivax Working Group.Malar J. 2017 Apr 5;16(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1784-1. Malar J. 2017. PMID: 28381261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing health equity for breastfeeding women: primaquine for Plasmodium vivax radical cure.Malar J. 2024 Sep 27;23(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12936-024-05112-9. Malar J. 2024. PMID: 39334094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in highly malaria-endemic municipalities in the Brazilian Amazon: A region-wide screening study.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022 May 26;12:100273. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2022.100273. eCollection 2022 Aug. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022. PMID: 36776424 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Operational Feasibility of Integrating Point-of-Care G6PD Testing into Plasmodium vivax Malaria Management in Vietnam.Pathogens. 2023 May 8;12(5):689. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050689. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37242359 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Current Status of G6PD Deficiency Testing to Guide Radical Cure Treatment for Vivax Malaria.Pathogens. 2023 Apr 27;12(5):650. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050650. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37242320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linked-evidence modelling of qualitative G6PD testing to inform low- and intermediate-dose primaquine treatment for radical cure of Plasmodium vivax.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Sep 5;18(9):e0012486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012486. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39236082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monteiro WM, Franca GP, Melo GC, Queiroz AL, Brito M, Peixoto HM, et al.. Clinical complications of G6PD deficiency in Latin American and Caribbean populations: systematic review and implications for malaria elimination programmes. Malar J. 2014;13: 70. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-70 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brito-Sousa JD, Santos TC, Avalos S, Fontecha G, Melo GC, Val F, et al.. Clinical Spectrum of Primaquine-induced Hemolysis in Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: A 9-Year Hospitalization-based Study From the Brazilian Amazon. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69: 1440–1442. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz122 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

