An improved nucleic acid sequence-based amplification method mediated by T4 gene 32 protein
- PMID: 35324960
- PMCID: PMC8947125
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265391
An improved nucleic acid sequence-based amplification method mediated by T4 gene 32 protein
Abstract
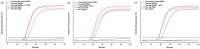
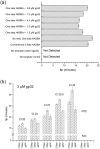
The uptake of Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification (NASBA) for point of care testing may be hindered by a complexity in the workflow due the requirement of a thermal denaturation step to initiate the cyclic isothermal amplification before the addition of the amplification enzymes. Despite reports of successful enhancement of other DNA and RNA amplification methods using DNA and RNA binding proteins, this has not been reported for NASBA. Here, three single-stranded binding proteins, RecA, Extreme Thermostable Single-stranded binding protein (ET SSB) and T4 gene gp32 protein (gp32), were incorporated in NASBA protocol and used for single pot, one-step NASBA at 41 °C. Indeed, all SSBs showed significantly improved amplifications compared with the 2-step process, but only gp32 showed no non-specific aberrant amplification, and slightly improved the time-to-positivity in comparison with the conventional NASBA. For synthetic HIV-1 RNA, gp32 was found to improve the time-to-positivity (ttp) by average of 13.6% of one-step NASBA and 6.7% of conventional NASBA for the detection of HIV-1 RNA, showing its potential for simplifying the workflow as desirable for point of care applications of NASBA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characteristics and applications of nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA).Mol Biotechnol. 2002 Feb;20(2):163-79. doi: 10.1385/MB:20:2:163. Mol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11876473 Review.
-
Ultrasensitive version of nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) utilizing a nicking and extension chain reaction system.Nanoscale. 2021 Jun 24;13(24):10785-10791. doi: 10.1039/d1nr00564b. Nanoscale. 2021. PMID: 34076022
-
Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Sep;41(9):4448-50. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.9.4448-4450.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12958290 Free PMC article.
-
NASBA isothermal enzymatic in vitro nucleic acid amplification optimized for the diagnosis of HIV-1 infection.J Virol Methods. 1991 Dec;35(3):273-86. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90069-c. J Virol Methods. 1991. PMID: 1726172
-
[Application of NASBA and RPA in detection of pathogenic bacteria].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Aug 10;40(8):1018-1022. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.08.027. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31484272 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1350. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021350. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279350 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic Acid Based Testing (NABing): A Game Changer Technology for Public Health.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2168-2200. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00870-4. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37695473 Review.
-
Medical viruses: diagnostic techniques.Virol J. 2023 Jul 11;20(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02108-w. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37434239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Virus Detection Techniques Based on Recombinant Polymerase Amplification.Molecules. 2024 Oct 21;29(20):4972. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204972. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoser MJ, Mansukoski HK, Morrical SW, Eboigbodin KE. Strand Invasion Based Amplification (SIBA (R)): A Novel Isothermal DNA Amplification Technology Demonstrating High Specificity and Sensitivity for a Single Molecule of Target Analyte. Plos One. 2014;9(11). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112656 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

