Identification of a Potent Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Antagonist
- PMID: 35325532
- PMCID: PMC9730857
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00086
Identification of a Potent Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Antagonist
Abstract
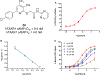
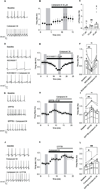
Human trace amine-associated receptor subtype 1 (hTAAR1) is a G protein-coupled receptor that has therapeutic potential for multiple diseases, including schizophrenia, drug addiction, and Parkinson's disease (PD). Although several potent agonists have been identified and have shown positive results in various clinical trials for schizophrenia, the discovery of potent hTAAR1 antagonists remains elusive. Herein, we report the results of structure-activity relationship studies that have led to the discovery of a potent hTAAR1 antagonist (RTI-7470-44, 34). RTI-7470-44 exhibited an IC50 of 8.4 nM in an in vitro cAMP functional assay, a Ki of 0.3 nM in a radioligand binding assay, and showed species selectivity for hTAAR1 over the rat and mouse orthologues. RTI-7470-44 displayed good blood-brain barrier permeability, moderate metabolic stability, and a favorable preliminary off-target profile. Finally, RTI-7470-44 increased the spontaneous firing rate of mouse VTA dopaminergic neurons and blocked the effects of the known TAAR1 agonist RO5166017. Collectively, this work provides a promising hTAAR1 antagonist probe that can be used to study TAAR1 pharmacology and the potential therapeutic role in hypodopaminergic diseases such as PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; cAMP functional assay; dopaminergic neurons; spontaneous firing rate; structure−activity relationship; trace amine-associated receptor 1 antagonist.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

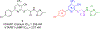
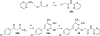
References
-
- Berry MD; Gainetdinov RR; Hoener MC; Shahid M, Pharmacology of human trace amine-associated receptors: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Pharmacol Ther 2017, 180, 161–180. - PubMed
-
- Borowsky B; Adham N; Jones KA; Raddatz R; Artymyshyn R; Ogozalek KL; Durkin MM; Lakhlani PP; Bonini JA; Pathirana S; Boyle N; Pu X; Kouranova E; Lichtblau H; Ochoa FY; Branchek TA; Gerald C, Trace amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98 (16), 8966–71. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindemann L; Ebeling M; Kratochwil NA; Bunzow JR; Grandy DK; Hoener MC, Trace amine-associated receptors form structurally and functionally distinct subfamilies of novel G protein-coupled receptors. Genomics 2005, 85 (3), 372–85. - PubMed
-
- Bunzow JR; Sonders MS; Arttamangkul S; Harrison LM; Zhang G; Quigley DI; Darland T; Suchland KL; Pasumamula S; Kennedy JL; Olson SB; Magenis RE; Amara SG; Grandy DK, Amphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, lysergic acid diethylamide, and metabolites of the catecholamine neurotransmitters are agonists of a rat trace amine receptor. Molecular pharmacology 2001, 60 (6), 1181–8. - PubMed
-
- Harmeier A; Obermueller S; Meyer CA; Revel FG; Buchy D; Chaboz S; Dernick G; Wettstein JG; Iglesias A; Rolink A; Bettler B; Hoener MC, Trace amine-associated receptor 1 activation silences GSK3beta signaling of TAAR1 and D2R heteromers. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2015, 25 (11), 2049–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

