Cerebrovascular reactivity deficits in cognitively unimpaired older adults: vasodilatory versus vasoconstrictive responses
- PMID: 35325813
- PMCID: PMC10958374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.02.006
Cerebrovascular reactivity deficits in cognitively unimpaired older adults: vasodilatory versus vasoconstrictive responses
Abstract
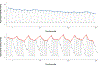
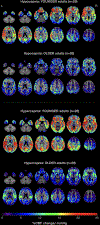
Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) deficits may index vulnerability to vascular brain injury and cognitive impairment, but findings on age-related changes in CVR have been mixed, and no studies to date have directly compared age-related changes in CVR to hypercapnia versus hypocapnia. The present study compared CVR in 31 cognitively unimpaired older adults (ages 55-87) and 30 healthy younger adults (ages 18-28). Breath control tasks induced CVR to hypocapnia (0.1 Hz paced breathing) and hypercapnia (15s breath holds) during pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling MRI. Relative to younger adults, cognitively unimpaired older adults displayed lower levels of global CVR under both hypocapnia and hypercapnia. In region-of-interest analyses, older adults exhibited attenuated CVR to hypocapnia in select frontal and temporal regions, and lower CVR to hypercapnia in all cortical, limbic, and subcortical regions examined, relative to younger adults. Results indicate age-related deficits in CVR are detectible even in cognitively unimpaired older adults and are disproportionately related to vasodilatory (hypercapnia) responses relative to vasoconstrictive (hypocapnia) responses. Findings may offer means for early detection of cerebrovascular dysfunction.
Keywords: Cerebral blood flow; Cerebrovascular reactivity; Cerebrovascular reserve; Hypercapnia; Hypocapnia; Older adults.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
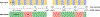
References
-
- Bondi MW, Edmonds EC, Jak AJ, Clark LR, Delano-Wood L, McDonald CR, Nation DA, Libon DJ, Au R, Galasko D, Salmon DP, 2014. Neuropsychological criteria for mild cognitive impairment improves diagnostic precision, biomarker associations, and progression rates. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 42, 275–289. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

