Interactions of melatonin, reactive oxygen species, and nitric oxide during fruit ripening: an update and prospective view
- PMID: 35325926
- PMCID: PMC9523826
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erac128
Interactions of melatonin, reactive oxygen species, and nitric oxide during fruit ripening: an update and prospective view
Abstract
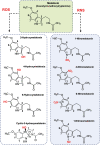
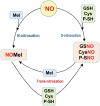
Fruit ripening is a physiological process that involves a complex network of signaling molecules that act as switches to activate or deactivate certain metabolic pathways at different levels, not only by regulating gene and protein expression but also through post-translational modifications of the involved proteins. Ethylene is the distinctive molecule that regulates the ripening of fruits, which can be classified as climacteric or non-climacteric according to whether or not, respectively, they are dependent on this phytohormone. However, in recent years it has been found that other molecules with signaling potential also exert regulatory roles, not only individually but also as a result of interactions among them. These observations imply the existence of mutual and hierarchical regulations that sometimes make it difficult to identify the initial triggering event. Among these 'new' molecules, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, and melatonin have been highlighted as prominent. This review provides a comprehensive outline of the relevance of these molecules in the fruit ripening process and the complex network of the known interactions among them.
Keywords: Hydrogen peroxide; melatonin; nitric oxide; nitrosomelatonin; postharvest; ripening.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures


References
-
- Aghdam MS, Luo Z, Li L, Jannatizadeh A, Fard JR, Pirzad F.. 2020a. Melatonin treatment maintains nutraceutical properties of pomegranate fruits during cold storage. Food Chemistry 303, 125385. - PubMed
-
- Aghdam MS, Palma JM, Corpas FJ.. 2020b. NADPH as a quality footprinting in horticultural crops marketability. Trends in Food Science & Technology 103, 152–161.
-
- Airaki M, Sánchez-Moreno L, Leterrier M, Barroso JB, Palma JM, Corpas FJ.. 2011. Detection and quantification of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plant organs by LC-ES/MS. Plant & Cell Physiology 52, 2006–2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

