Reticular epithelial corneal edema as a novel side-effect of Rho Kinase Inhibitors: An Indian scenario
- PMID: 35326007
- PMCID: PMC9240559
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2865_21
Reticular epithelial corneal edema as a novel side-effect of Rho Kinase Inhibitors: An Indian scenario
Abstract
Purpose: To describe clinical course, characteristics, and outcome of reticular epithelial corneal edema (RECE) occurring as a not-so-infrequent adverse effect of a novel drug, Rho-kinase inhibitors (ROCK-I)- netarsudil (0.02%) and ripasudil (0.4%).
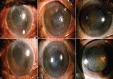
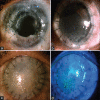
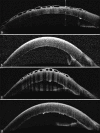
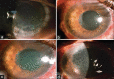
Methods: This was a retrospective observational non-randomized study. In this study, 12 eyes of 11 patients presenting at a tertiary eye care center between April 2021 and September 2021 were included. All 12 eyes developed a distinctive honeycomb pattern of RECE after starting topical ROCK-I. All patients were subjected to detailed ophthalmic examinations.
Results: Eight patients were started on netarsudil (0.02%) and three on ripasudil (0.4%). Five eyes had a prior history of corneal edema. The remaining seven had the presence of ocular comorbidities predisposing to corneal edema. The average time for RECE occurrence was 25 days for netarsudil and 82 days for ripasudil. Visual acuity decreased in two eyes, remained unaffected in four eyes, and could not be quantified in four eyes due to preexisting profound visual impairment. Five eyes had symptoms of ocular surface discomfort associated with bullae. Symptoms and bullae resolved in all eyes in whom ROCK-I was stopped. The average time to resolution of RECE was 10 days for netarsudil and 25 days for ripasudil.
Conclusion: RECE after ROCK-I occurs with the use of both netarsudil and ripasudil, although the characteristics differ. The presence of corneal edema and endothelial decompensation seem to be a risk factor, and cautious use is warranted in these patients. Four clinical stages of RECE are described. ROCK-I act as a double-edged sword in patients with endothelial decompensation. Large-scale studies are required to know the exact incidence, pathophysiology, and long-term consequences of the aforementioned side-effect.
Keywords: Anterior segment optical coherence tomography; honeycomb edema; reticular epithelial corneal edema; rho-kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drug- and Cell-Type-Specific Effects of ROCK Inhibitors as a Potential Cause of Reticular Corneal Epithelial Edema.Cells. 2025 Feb 11;14(4):258. doi: 10.3390/cells14040258. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996731 Free PMC article.
-
Netarsudil-associated reticular corneal epithelial edema.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022 Jan 20;25:101287. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101287. eCollection 2022 Mar. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35146185 Free PMC article.
-
Reticular Epithelial Edema: An Uncommon Side Effect of ROCK/NET Inhibitor Netarsudil.J Glaucoma. 2020 Nov;29(11):e124-e126. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001636. J Glaucoma. 2020. PMID: 32826765
-
The Role of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jan 19;18:97-108. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S435522. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38264539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Honeycomb Epithelial Edema Associated With Rho Kinase Inhibition: A Case Series and Review of the Literature.Cornea. 2022 Feb 1;41(2):243-248. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002694. Cornea. 2022. PMID: 35037906 Review.
Cited by
-
A Narrative Review of Ocular Surface Disease Related to Anti-Glaucomatous Medications.Ophthalmol Ther. 2022 Oct;11(5):1681-1704. doi: 10.1007/s40123-022-00557-0. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Ophthalmol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35943668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Role of Rho-Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases.Life (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;15(8):1283. doi: 10.3390/life15081283. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular effects of Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibition: a systematic review.Eye (Lond). 2024 Dec;38(18):3418-3428. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03342-4. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39285241
-
Drug- and Cell-Type-Specific Effects of ROCK Inhibitors as a Potential Cause of Reticular Corneal Epithelial Edema.Cells. 2025 Feb 11;14(4):258. doi: 10.3390/cells14040258. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996731 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases and Glaucoma-A Comprehensive Review of These Emerging Drugs.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 25;12(21):6736. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216736. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garnock-Jones KP. Ripasudil: First global approval. Drugs. 2014;74:2211–5. - PubMed
-
- Hoy SM. Netarsudil ophthalmic solution 0.02%: First global approval. Drugs. 2018;78:389–96. - PubMed
-
- Toris CB, McLaughlin MA, Dworak DP, Fan S, Havens S, Zhan GL, et al. Effects of Rho Kinase inhibitors on intraocular pressure and aqueous humor dynamics in nonhuman primates and rabbits. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2016;32:355–64. - PubMed
-
- Wang RF, Williamson JE, Kopczynski C, Serle JB. Effect of 0.04% AR-13324, a ROCK, and norepinephrine transporter inhibitor, on aqueous humor dynamics in normotensive monkey eyes. J Glaucoma. 2015;24:51–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

