Role of Oxidative Stress in Vascular Low-Grade Inflammation Initiation Due to Acute Salt Loading in Young Healthy Individuals
- PMID: 35326095
- PMCID: PMC8944840
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030444
Role of Oxidative Stress in Vascular Low-Grade Inflammation Initiation Due to Acute Salt Loading in Young Healthy Individuals
Abstract
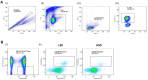
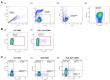
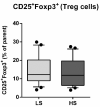
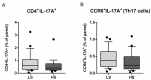
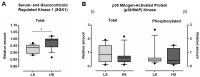
This study aimed to investigate the effect of 7-day high-salt (HS) and the specific role of oxidative stress on vascular low-grade inflammation initiation in young salt-resistant healthy individuals. 30 young healthy individuals adhered to a 7-day low-salt (LS) diet (3.5 g salt/day), followed by a 7-day high-salt (HS) diet (~14.7 g salt/day) protocol. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, frequencies of peripheral blood Th17 and Treg cells, Th17/Treg ratio, enzymes SGK1, and p38/MAP kinase, as well as biomarkers of endothelial activation and oxidative stress, were measured before and after the 7-day HS diet protocol. Short-term HS diet significantly increased serum level of pro-inflammatory cytokines INF-γ, TNF-α, IL-9, and IL-17A levels, but also of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β1. Relative amount of total SGK1 significantly increased, following the 7-day HS diet. Increased oxidative stress level, following HS diet, was negatively associated with the frequency of Treg cells. The increase in relative amount of total SGK1 in peripheral mononuclear cells following 7-day HS diet suggests lymphocyte (re)activation, in response to HS intake, resulting in enhanced production of pro-inflammatory (IL-17, INF-γ), but also anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β1). Increased oxidative stress, due to HS loading, alters immune regulatory mechanisms, presumably via effects on Treg cells.
Keywords: Th17 cells; cell adhesion molecules; cytokines; endothelium; high-salt diet; inflammation; oxidative stress; regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative Stress Induced by High Salt Diet-Possible Implications for Development and Clinical Manifestation of Cutaneous Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in Psoriasis vulgaris.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;11(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071269. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is There Association between Altered Adrenergic System Activity and Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by a 7-Day High Salt Intake in Young Healthy Individuals.Nutrients. 2021 May 20;13(5):1731. doi: 10.3390/nu13051731. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34065261 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Attenuated flow-induced dilatation of middle cerebral arteries is related to increased vascular oxidative stress in rats on a short-term high salt diet.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;594(17):4917-31. doi: 10.1113/JP272297. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27061200 Free PMC article.
-
Early Low-Grade Inflammation Induced by High-Salt Diet in Sprague Dawley Rats Involves Th17/Treg Axis Dysregulation, Vascular Wall Remodeling, and a Shift in the Fatty Acid Profile.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024 Feb 27;58(1):83-103. doi: 10.33594/000000684. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38459804
-
T helper 17 cell/regulatory T-cell imbalance in hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: the link to hair follicle dissection, obesity, smoking and autoimmune comorbidities.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;179(2):260-272. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16561. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29573406 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-Week Low-Salt Diet Improves Acetylcholine-Induced Microvascular Dilation in Biologically Naïve Psoriasis Patients.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 14;17(4):693. doi: 10.3390/nu17040693. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40005022 Free PMC article.
-
Tff3-/- Knock-Out Mice with Altered Lipid Metabolism Exhibit a Lower Level of Inflammation following the Dietary Intake of Sodium Chloride for One Week.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 15;24(8):7315. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087315. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108475 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II Exposure In Vitro Reduces High Salt-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Modulates Cell Adhesion Molecules' Expression in Human Aortic Endothelial Cell Line.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 29;12(12):2741. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122741. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767646 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nitric Oxide in the Micro- and Macrovascular Response to a 7-Day High-Salt Diet in Healthy Individuals.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7157. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087157. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108318 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Induced by High Salt Diet-Possible Implications for Development and Clinical Manifestation of Cutaneous Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in Psoriasis vulgaris.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;11(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071269. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boegehold M.A., Drenjancevic I., Lombard J.H. Comprehensive Physiology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2015. Salt, Angiotensin II, superoxide, and endothelial function; pp. 215–254. - PubMed
-
- Barić L., Drenjančević I., Matić A., Stupin M., Kolar L., Mihaljević Z., Lenasi H., Šerić V., Stupin A. Seven-Day salt loading impairs microvascular endothelium-dependent vasodilation without changes in blood pressure, body composition and fluid status in healthy young humans. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019;44:835–847. doi: 10.1159/000501747. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

