Venetoclax-Resistant MV4-11 Leukemic Cells Activate PI3K/AKT Pathway for Metabolic Reprogramming and Redox Adaptation for Survival
- PMID: 35326111
- PMCID: PMC8944541
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030461
Venetoclax-Resistant MV4-11 Leukemic Cells Activate PI3K/AKT Pathway for Metabolic Reprogramming and Redox Adaptation for Survival
Abstract
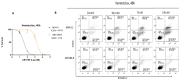
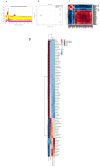
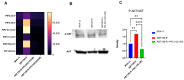
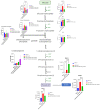
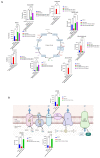
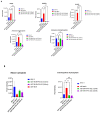
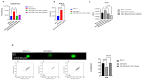
Venetoclax (ABT199) is a selective B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor. The US FDA recently approved it to be used in combination with low-dose cytarabine or hypomethylating agents in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or elderly patients non-eligible for chemotherapy. However, acquiring resistance to venetoclax in AML patients is the primary cause of treatment failure. To understand the molecular mechanisms inherent in the resistance to BCL-2 inhibitors, we generated a venetoclax-resistant cell line model and assessed the consequences of this resistance on its metabolic pathways. Untargeted metabolomics data displayed a notable impact of resistance on the PI3K/AKT pathway, the Warburg effect, glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and redox metabolism. The resistant cells showed increased NADPH and reduced glutathione levels, switching their energy metabolism towards glycolysis. PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition shifted resistant cells towards oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Our results provide a metabolic map of resistant cells that can be used to design novel metabolic targets to challenge venetoclax resistance in AML.
Keywords: MV4-11; OXPHOS; PI3K/AKT pathway; acute myeloid leukemia; glycolysis; metabolomics; redox metabolism; venetoclax; venetoclax resistance model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gandhi L., Camidge D.R., de Oliveira M.R., Bonomi P., Gandara D., Khaira D., Hann C.L., McKeegan E.M., Litvinovich E., Hemken P.M., et al. Phase I Study of Navitoclax (ABT-263), a Novel Bcl-2 Family Inhibitor, in Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Other Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:909–916. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.6208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Souers A.J., Leverson J.D., Boghaert E.R., Ackler S.L., Catron N.D., Chen J., Dayton B.D., Ding H., Enschede S.H., Fairbrother W.J., et al. ABT-199, a Potent and Selective BCL-2 Inhibitor, Achieves Antitumor Activity While Sparing Platelets. Nat. Med. 2013;19:202–208. doi: 10.1038/nm.3048. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

