Polyphenol Rich Forsythia suspensa Extract Alleviates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice through the Nrf2-NLRP3 Pathway
- PMID: 35326124
- PMCID: PMC8944444
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030475
Polyphenol Rich Forsythia suspensa Extract Alleviates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice through the Nrf2-NLRP3 Pathway
Abstract
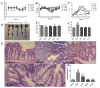
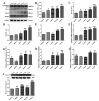
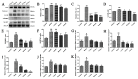
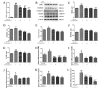
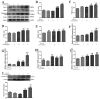
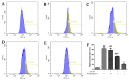
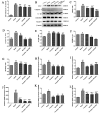
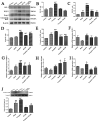
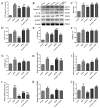
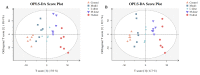
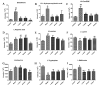
This study systematically evaluated the effect of Forsythia suspensa extract on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis (UC) and determined its mechanism of action. The results showed that Forsythia suspensa extract significantly inhibited DSS-induced UC in mice. In vivo mechanistic studies revealed that Forsythia suspensa extract relieved the symptoms of colitis by enhancing antioxidant activity and inhibiting pyroptosis. Further in vitro experiments on the mechanism of Forsythia suspensa showed that it reduced the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in J774A.1 cells. We found that Forsythia suspensa extract enhanced cellular antioxidation activity and inhibited pyroptosis. After silencing NLRP3, it was found to play an important role in pyroptosis. In addition, after Nrf2 was silenced, the inhibitory effect of Forsythia suspensa extract on cell pyroptosis was eliminated, indicating an interaction between Nrf2 and NLRP3. Metabonomics revealed that Forsythia suspensa extract significantly improved metabolic function in colitis mice by reversing the abnormal changes in the levels of 9 metabolites. The main metabolic pathways involved were glutathione metabolism, aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis and linoleic acid metabolism. In conclusion, we found that Forsythia suspensa extract significantly alleviated DSS-induced UC injury through the Nrf2-NLRP3 pathway and relieved metabolic dysfunction.
Keywords: Forsythia suspensa; antioxidant; metabolomics; pyroptosis; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
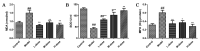
Similar articles
-
Forsythia suspensa polyphenols regulate macrophage M1 polarization to alleviate intestinal inflammation in mice.Phytomedicine. 2024 Mar;125:155336. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155336. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38295660
-
Isofraxidin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through inhibiting pyroptosis by upregulating Nrf2 and reducing reactive oxidative species.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;128:111570. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111570. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38280336
-
Shaoyao decoction attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, macrophage and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the MKP1/NF-κB pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 Nov;92:153743. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153743. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34583225
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and future research of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:318-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.040. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28887216 Review.
-
Efficacy of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl on mouse and rat models of inflammation-related diseases: a meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1288584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1288584. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38500762 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Natural compounds target programmed cell death (PCD) signaling mechanism to treat ulcerative colitis: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 9;15:1333657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1333657. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38405669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Gut Microbiota Modulation Potentials of Flavonoids Extracted from Passiflora foetida Fruits.Foods. 2023 Jul 29;12(15):2889. doi: 10.3390/foods12152889. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37569158 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Chinese Medicine in Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Aug;29(8):750-760. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3551-1. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37148482 Review.
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: role of polyphenols.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 21;14:1185317. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1185317. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37545494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of the Proprietary Chinese Medicine "JiuLiWan" to Treat Ulcerative Colitis Revealed by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification In Vitro.ACS Omega. 2025 May 6;10(19):19598-19613. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00261. eCollection 2025 May 20. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40415848 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

