Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy
- PMID: 35326161
- PMCID: PMC8944751
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030511
Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy
Abstract
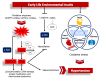
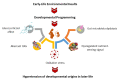
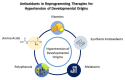
Hypertension remains the leading cause of disease burden worldwide. Hypertension can originate in the early stages of life. A growing body of evidence suggests that oxidative stress, which is characterized as a reactive oxygen species (ROS)/nitric oxide (NO) disequilibrium, has a pivotal role in the hypertension of developmental origins. Results from animal studies support the idea that early-life oxidative stress causes developmental programming in prime blood pressure (BP)-controlled organs such as the brain, kidneys, heart, and blood vessels, leading to hypertension in adult offspring. Conversely, perinatal use of antioxidants can counteract oxidative stress and therefore lower BP. This review discusses the interaction between oxidative stress and developmental programming in hypertension. It will also discuss evidence from animal models, how oxidative stress connects with other core mechanisms, and the potential of antioxidant therapy as a novel preventive strategy to prevent the hypertension of developmental origins.
Keywords: antioxidant; asymmetric dimethylarginine; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD); hypertension; nitric oxide; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; renin-angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease: Why Oxidative Stress Matters?Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;10(1):33. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010033. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Syndrome Programming and Reprogramming: Mechanistic Aspects of Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;11(11):2108. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112108. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Origins of Hypertension: Should Prevention Start Before Birth Using Natural Antioxidants?Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 23;9(11):1034. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111034. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33113999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental and Early Life Origins of Hypertension: Preventive Aspects of Melatonin.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 8;11(5):924. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050924. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Consideration of Gut Microbiome in Animal Models.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 9;10(4):875. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040875. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of haptoglobin genotype on the association of asymmetric dimethylarginine and DDAH 1 polymorphism with diabetic macroangiopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Dec 2;21(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01702-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36461077 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomechanisms of Prenatally Programmed Adult Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;12(7):1354. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071354. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking oxidative stress biomarkers to disease progression and antioxidant therapy in hypertension and diabetes mellitus.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 26;12:1611842. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1611842. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40492113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the bioactivity of MicroRNAs Originated from Plant-derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles (PELNs): current perspectives.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Aug 12;23(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03602-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40796868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of the R-(+)-thioctic acid treatment: possible anti-inflammatory activity on heart of hypertensive rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 24;24(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04547-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39048980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Hypertension. 2019. [(accessed on 10 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

