Activation of the Nrf2 Pathway Prevents Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Caspase-3 Cleaved Tau: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35326165
- PMCID: PMC8944569
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030515
Activation of the Nrf2 Pathway Prevents Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Caspase-3 Cleaved Tau: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
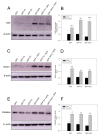
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by memory and cognitive impairment, accompanied by the accumulation of extracellular deposits of amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) and the presence of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of pathological forms of tau protein. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are also critical elements for AD development. We previously showed that the presence of caspase-3 cleaved tau, a relevant pathological form of tau in AD, induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in different neuronal models. Recent studies demonstrated that the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) plays a significant role in the antioxidant response promoting neuroprotection. Here, we studied the effects of Nrf2 activation using sulforaphane (SFN) against mitochondrial injury induced by caspase-3 cleaved tau. We used immortalized cortical neurons to evaluate mitochondrial bioenergetics and ROS levels in control and SFN-treated cells. Expression of caspase-3 cleaved tau induced mitochondrial fragmentation, depolarization, ATP loss, and increased ROS levels. Treatment with SFN for 24 h significantly prevented these mitochondrial abnormalities, and reduced ROS levels. Analysis of Western blots and rt-PCR studies showed that SFN treatment increased the expression of several Nrf2-related antioxidants genes in caspase-3 cleaved tau cells. These results indicate a potential role of the Nrf2 pathway in preventing mitochondrial dysfunction induced by pathological forms of tau in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Nrf2; antioxidant; mitochondrial dysfunction; neuroprotection; sulforaphane; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathological Impact of Tau Proteolytical Process on Neuronal and Mitochondrial Function: a Crucial Role in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5691-5707. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03434-4. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37332018 Review.
-
Sulforaphane prevents cognitive decline and mitochondrial failure induced by hippocampal expression of caspase-3 cleaved tau.Neurochem Int. 2025 Jul;187:105991. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2025.105991. Epub 2025 May 6. Neurochem Int. 2025. PMID: 40339911
-
Truncated Tau Induces Mitochondrial Transport Failure Through the Impairment of TRAK2 Protein and Bioenergetics Decline in Neuronal Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jul 30;14:175. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00175. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848607 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-3 cleaved tau impairs mitochondrial function through the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Jan;1870(1):166898. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166898. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 37774936 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Mitochondria: An Early Target of Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;84(4):1391-1414. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215139. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34719499 Review.
Cited by
-
The use of fibroblasts as a valuable strategy for studying mitochondrial impairment in neurological disorders.Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Jul 4;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00308-y. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35787292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular PHF-tau modulates astrocyte mitochondrial dynamics and mediates neuronal connectivity.Transl Neurodegener. 2025 Mar 24;14(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40035-025-00474-9. Transl Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40122883 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin (Trx): A redox target and modulator of cellular senescence and aging-related diseases.Redox Biol. 2024 Apr;70:103032. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103032. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38232457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Impact of Tau Proteolytical Process on Neuronal and Mitochondrial Function: a Crucial Role in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5691-5707. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03434-4. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37332018 Review.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Oxidative Stress Through the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway to Improve Alzheimer Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Mar;62(3):3493-3507. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04498-6. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39299981 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed Z., Cooper J., Murray T.K., Garn K., McNaughton E., Clarke H., Parhizkar S., Ward M.A., Cavallini A., Jackson S., et al. A Novel in Vivo Model of Tau Propagation with Rapid and Progressive Neurofibrillary Tangle Pathology: The Pattern of Spread Is Determined by Connectivity, Not Proximity. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127:667–683. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1254-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

