Exploring the Use of Iris Species: Antioxidant Properties, Phytochemistry, Medicinal and Industrial Applications
- PMID: 35326175
- PMCID: PMC8944787
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030526
Exploring the Use of Iris Species: Antioxidant Properties, Phytochemistry, Medicinal and Industrial Applications
Abstract
The genus Iris from the Iridaceae family consists of more than 262 recognized species. It is an ornamental and medicinal plant widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere. Iris species convey a long history as valuable traditional drugs with a wide variety of applications in various cultures, having been recorded since medieval times. Currently, Iris spp. still find application in numerous fields, including cosmetics, pharmaceutics and the food industry. Moreover, many of their empirical uses have been validated by in vitro and in vivo studies, showing that Iris spp. exhibit potent antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective and anti-microbial properties. Phytochemicals investigations have revealed that the plant extracts are rich in phenolic compounds, especially flavonoids and phenolic acids. As such, they constitute a promising lead for seeking new drugs with high susceptibilities towards various health issues, particularly oxidative-stress-related diseases such as cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, etc. Herein, we present a literature review of the genus Iris intending to determine the plant's chemical profile and establish a coherent overview of the biological applications of the plant extracts with reference to their traditional uses.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; ethnobotanical uses; genus Iris; pharmacological activities; phytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

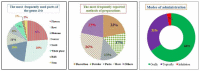
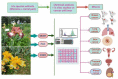
Similar articles
-
Traditional uses, ten-years research progress on phytochemistry and pharmacology, and clinical studies of the genus Scutellaria.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 30;265:113198. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113198. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32739568
-
Genus Paeonia: A comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113708. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113708. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33346027 Review.
-
A review of the traditional uses, phytochemistry and biological activities of the Melastoma genus.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 10;264:113322. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113322. Epub 2020 Aug 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32871236
-
The genus Nepeta: Traditional uses, phytochemicals and pharmacological properties.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113679. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113679. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33307050 Review.
-
Traditional medicinal uses, pharmacology, phytochemistry, and distribution of the Genus Fagaropsis (Rutaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114781. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114781. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34715298 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical characterization and biomedical potential of Iris kashmiriana flower extracts: a promising source of natural antioxidants and cytotoxic agents.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 21;14(1):24785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58362-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39433747 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Tigridia vanhouttei Extracts.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 31;12(17):3136. doi: 10.3390/plants12173136. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687382 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of 76 Plant Species Collected in Andalusia (Spain) against Lung Cancer Cells.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;12(18):3275. doi: 10.3390/plants12183275. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765439 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling, antioxidant, and enzyme inhibition potential of Iris pseudacorus L. from Egypt and Japan: A comparative study.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 30;13(1):5233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32224-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36997571 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal plants and their derivatives for skin and hair: a Mediterranean perspective of women care.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Apr 13;317(1):710. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04202-1. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40221958 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Van Wyk B.-E., Wink M. Phytomedicines, Herbal Drugs, and Poisons. The University of Chicago Press; Chicago, IL, USA: 2015. pp. 1–304.
-
- Zougagh S., Belghiti A., Rochd T., Zerdani I., Mouslim J. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Used in Traditional Treatment of the Oral Pathology: The Ethnobotanical Survey in the Economic Capital Casablanca, Morocco (North Africa) Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2019;9:35–48. doi: 10.1007/s13659-018-0194-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fan L., Gao Y., Hasenstein K.H., Wang L. ‘Flower Angel’: A New Iris sanguinea Cultivar. HortScience. 2021;56:617–618. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI15703-21. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

