Ginkgo biloba in the Aging Process: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35326176
- PMCID: PMC8944638
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030525
Ginkgo biloba in the Aging Process: A Narrative Review
Abstract
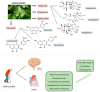
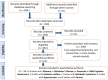
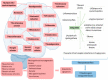
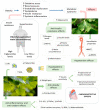
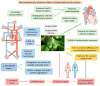
Neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease (CVD), hypertension, insulin resistance, cancer, and other degenerative processes commonly appear with aging. Ginkgo biloba (GB) is associated with several health benefits, including memory and cognitive improvement, in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and cancer. Its antiapoptotic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory actions have effects on cognition and other conditions associated with aging-related processes, such as insulin resistance, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions. The aim of this study was to perform a narrative review of the effects of GB in some age-related conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases, CVD, and cancer. PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase databases were searched, and the PRISMA guidelines were applied. Fourteen clinical trials were selected; the studies showed that GB can improve memory, cognition, memory scores, psychopathology, and the quality of life of patients. Moreover, it can improve cerebral blood flow supply, executive function, attention/concentration, non-verbal memory, and mood, and decrease stress, fasting serum glucose, glycated hemoglobin, insulin levels, body mass index, waist circumference, biomarkers of oxidative stress, the stability and progression of atherosclerotic plaques, and inflammation. Therefore, it is possible to conclude that the use of GB can provide benefits in the prevention and treatment of aging-related conditions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Gingko biloba; aging; cancer; cardiovascular disease; metabolic syndrome; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barbalho S.M., Flato U.A.P., Tofano R.J., Goulart R.A., Guiguer E.L., Detregiachi C.R.P., Buchaim D.V., Araújo A.C., Buchaim R.L., Reina F.T.R., et al. Physical Exercise and Myokines: Relationships with Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:3607. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103607. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morvaridzadeh M., Fazelian S., Agah S., Khazdouz M., Rahimlou M., Agh F., Potter E., Heshmati S., Heshmati J.J.C. Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) on inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cytokine. 2020;135:155224. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155224. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grewal A.K., Singh T.G., Sharma D., Sharma V., Singh M., Rahman M.H., Najda A., Walasek-Janusz M., Kamel M., Albadrani G.M., et al. Mechanistic insights and perspectives involved in nfeuroprotective action of quercetin. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021;140:111729. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111729. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

