Piperine Attenuates Lithocholic Acid-Stimulated Interleukin-8 by Suppressing Src/EGFR and Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35326180
- PMCID: PMC8944659
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030530
Piperine Attenuates Lithocholic Acid-Stimulated Interleukin-8 by Suppressing Src/EGFR and Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
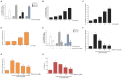
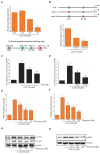
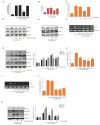
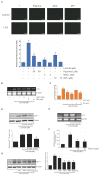
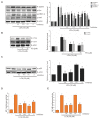
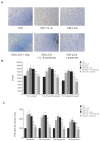
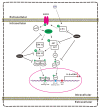
Piperine, a natural alkaloidal pungent product present in pepper plants, possesses the properties of anti-inflammatory and anti-metastasis. Lithocholic acid is a monohydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid with an alpha-hydroxy substituent at position 3; it is a secondary bile acid that plays a pivotal role in fat absorption, and has been discovered to mediate colorectal cancer (CRC) cell invasion and migration. However, the effect of piperine on angiogenesis has been poorly investigated. In the current study, we examined the role of piperine on LCA-stimulated angiogenesis by measuring interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression; moreover, we revealed the potential molecular mechanisms in CRC cells. Here, we showed that piperine inhibited LCA-stimulated endothelial EA.hy926 cell angiogenesis in a conditioned medium obtained from colorectal HCT-116 cells. Experiments with an IL-8 neutralizer showed that IL-8 present in the conditioned medium was the major angiogenic factor. Piperine inhibited LCA-stimulated ERK1/2 and AKT via the Src/EGFR-driven ROS signaling pathway in the colorectal cell line (HCT-116). Through mutagenesis and inhibitory studies, we revealed that ERK1/2 acted as an upstream signaling molecule in AP-1 activation, and AKT acted as an upstream signaling molecule in NF-κB activation, which in turn attenuated IL-8 expression. Taken together, we demonstrated that piperine blocked LCA-stimulated IL-8 expression by suppressing Src and EGFR in human CRC HCT-116 cells, thus remarkably attenuating endothelial EA.hy926 cell tube formation.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; interleukin-8; piperine; reactive oxygen species; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper. Authors Thi Thinh Nguyen and Trong Thuan Ung are from Nanogen Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Joint Stock Company, the company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Andrographolide Antagonizes TNF-α-Induced IL-8 via Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase/ROS/NF-κB and Src/MAPKs/AP-1 Axis in Human Colorectal Cancer HCT116 Cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 May 23;66(20):5139-5148. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00810. Epub 2018 May 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29672044
-
Metformin inhibits lithocholic acid-induced interleukin 8 upregulation in colorectal cancer cells by suppressing ROS production and NF-kB activity.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 14;9(1):2003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38778-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30765814 Free PMC article.
-
Lithocholic Acid Stimulates IL-8 Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells Via Activation of Erk1/2 MAPK and Suppression of STAT3 Activity.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Sep;118(9):2958-2967. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25955. Epub 2017 May 3. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28247965
-
The roles of microbial products in the development of colorectal cancer: a review.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):720-735. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1889109. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33618627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piperine as a Potential Anti-cancer Agent: A Review on Preclinical Studies.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(37):4918-4928. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170523120656. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28545378 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Lithocholic Acid on the Gut-Liver Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 7;13:910493. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.910493. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulforaphane Inhibits IL-1β-Induced IL-6 by Suppressing ROS Production, AP-1, and STAT3 in Colorectal Cancer HT-29 Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 28;13(4):406. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040406. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671854 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide suppresses IL-1β-induced expression of interleukin-8 by inhibiting ROS-Mediated ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB molecules in human gastric cancer AGS cells.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 30;14:1498213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1498213. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39950099 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystectomy promotes the development of colorectal cancer by the alternation of bile acid metabolism and the gut microbiota.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 23;9:1000563. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1000563. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213655 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane Suppresses the Nicotine-Induced Expression of the Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 via Inhibiting ROS-Mediated AP-1 and NF-κB Signaling in Human Gastric Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 5;23(9):5172. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095172. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hwang Y.S., Jeong M., Park J.S., Kim M.H., Lee D.B., Shin B.A., Mukaida N., Ellis L.M., Kim H.R., Ahn B.W., et al. Interleukin-1beta stimulates IL-8 expression through MAP kinase and ROS signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:6603–6611. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207867. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

