Vitamin Supplements as a Nutritional Strategy against Chronic Alcohol Consumption? An Updated Review
- PMID: 35326214
- PMCID: PMC8945215
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030564
Vitamin Supplements as a Nutritional Strategy against Chronic Alcohol Consumption? An Updated Review
Abstract
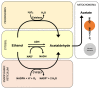
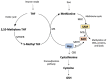
Several studies have shown that blood vitamin levels are low in alcoholic patients. In effect, alcohol use abuse is considered a chronic disease that promotes the pathogenesis of many fatal diseases, such as cancer and liver cirrhosis. The alcohol effects in the liver can be prevented by antioxidant mechanisms, which induces enzymatic as well as other nonenzymatic pathways. The effectiveness of several antioxidants has been evaluated. However, these studies have been accompanied by uncertainty as mixed results were reported. Thus, the aim of the present review article was to examine the current knowledge on vitamin deficiency and its role in chronic liver disease. Our review found that deficiencies in nutritional vitamins could develop rapidly during chronic liver disease due to diminished hepatic storage and that inadequate vitamins intake and alcohol consumption may interact to deplete vitamin levels. Numerous studies have described that vitamin supplementation could reduce hepatotoxicity. However, further studies with reference to the changes in vitamin status and the nutritional management of chronic liver disease are in demand.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease; vitamin B1; vitamin C; vitamin D; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

