A PON for All Seasons: Comparing Paraoxonase Enzyme Substrates, Activity and Action including the Role of PON3 in Health and Disease
- PMID: 35326240
- PMCID: PMC8945423
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030590
A PON for All Seasons: Comparing Paraoxonase Enzyme Substrates, Activity and Action including the Role of PON3 in Health and Disease
Abstract
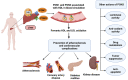
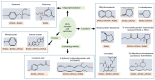
Paraoxonases (PONs) are a family of hydrolytic enzymes consisting of three members, PON1, PON2, and PON3, located on human chromosome 7. Identifying the physiological substrates of these enzymes is necessary for the elucidation of their biological roles and to establish their applications in the biomedical field. PON substrates are classified as organophosphates, aryl esters, and lactones based on their structure. While the established native physiological activity of PONs is its lactonase activity, the enzymes' exact physiological substrates continue to be elucidated. All three PONs have antioxidant potential and play an important anti-atherosclerotic role in several diseases including cardiovascular diseases. PON3 is the last member of the family to be discovered and is also the least studied of the three genes. Unlike the other isoforms that have been reviewed extensively, there is a paucity of knowledge regarding PON3. Thus, the current review focuses on PON3 and summarizes the PON substrates, specific activities, kinetic parameters, and their association with cardiovascular as well as other diseases such as HIV and cancer.
Keywords: HIV; cancer; cardiovascular disease; lactones; paraoxonase; substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
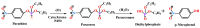
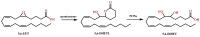
Similar articles
-
Identification of biologically active δ-lactone eicosanoids as paraoxonase substrates.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 20;505(1):87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.083. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30241945
-
The Structure and Function of Paraoxonase-1 and Its Comparison to Paraoxonase-2 and -3.Molecules. 2020 Dec 17;25(24):5980. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245980. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33348669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human paraoxonases (PON1, PON2, and PON3) are lactonases with overlapping and distinct substrate specificities.J Lipid Res. 2005 Jun;46(6):1239-47. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M400511-JLR200. Epub 2005 Mar 16. J Lipid Res. 2005. PMID: 15772423
-
Paraoxonases function as unique protectors against cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: Updated experimental and clinical data.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Aug;239(8):899-906. doi: 10.1177/1535370214535897. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014. PMID: 24903163
-
Pharmacogenetics of paraoxonases: a brief review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;369(1):78-88. doi: 10.1007/s00210-003-0833-1. Epub 2003 Oct 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14579013 Review.
Cited by
-
The Analysis of Plasma Proteomics for Luminal A Breast Cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Dec;13(23):e70470. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70470. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39641443 Free PMC article.
-
Paraoxonases at the Heart of Neurological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6881. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086881. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Phototherapy in Atopic Dermatitis: Mechanisms, Role, and Future Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 19;12(12):1904. doi: 10.3390/biom12121904. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Exploration of Paraoxonase 1 Function in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7764. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097764. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraoxonase 1: evolution of the enzyme and of its role in protecting against atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024 Aug 1;35(4):171-178. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000936. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024. PMID: 38887979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harel M., Aharoni A., Gaidukov L., Brumshtein B., Khersonsky O., Meged R., Dvir H., Ravelli R.B., McCarthy A., Toker L., et al. Structure and evolution of the serum paraoxonase family of detoxifying and anti-atherosclerotic enzymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:412–419. doi: 10.1038/nsmb767. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

