Calcium Channels in the Heart: Disease States and Drugs
- PMID: 35326393
- PMCID: PMC8945986
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11060943
Calcium Channels in the Heart: Disease States and Drugs
Abstract
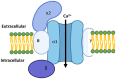
Calcium ions are the major signaling ions in the cells. They regulate muscle contraction, neurotransmitter secretion, cell growth and migration, and the activity of several proteins including enzymes and ion channels and transporters. They participate in various signal transduction pathways, thereby regulating major physiological functions. Calcium ion entry into the cells is regulated by specific calcium channels and transporters. There are mainly six types of calcium channels, of which only two are prominent in the heart. In cardiac tissues, the two types of calcium channels are the L type and the T type. L-type channels are found in all cardiac cells and T-type are expressed in Purkinje cells, pacemaker and atrial cells. Both these types of channels contribute to atrioventricular conduction as well as pacemaker activity. Given the crucial role of calcium channels in the cardiac conduction system, mutations and dysfunctions of these channels are known to cause several diseases and disorders. Drugs targeting calcium channels hence are used in a wide variety of cardiac disorders including but not limited to hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias. This review summarizes the type of cardiac calcium channels, their function, and disorders caused by their mutations and dysfunctions. Finally, this review also focuses on the types of calcium channel blockers and their use in a variety of cardiac disorders.
Keywords: arrhythmia; calcium channel blockers; calcium channels; calcium ions; cardiac function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcium channel diversity in the cardiovascular system.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Aug;28(2):522-9. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(96)00170-2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8800134 Review.
-
T-type channels in the sino-atrial and atrioventricular pacemaker mechanism.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Apr;466(4):791-9. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1482-6. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24573175 Review.
-
Why are some antiarrhythmic drugs proarrhythmic? Cardiac arrhythmia study by bifurcation analysis.J Electrocardiol. 1995;28 Suppl:191-7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(95)80055-7. J Electrocardiol. 1995. PMID: 8656110
-
Both T- and L-type Ca2+ channels can contribute to excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac Purkinje cells.Biophys J. 1998 Apr;74(4):1830-9. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77893-2. Biophys J. 1998. PMID: 9545045 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia, arrhythmia and ion-channel gene defects.Trends Genet. 1998 Mar;14(3):92-8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(97)01370-x. Trends Genet. 1998. PMID: 9540405 Review.
Cited by
-
Antihypertensive Effects of Lindera erythrocarpa Makino via NO/cGMP Pathway and Ca2+ and K+ Channels.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 5;16(17):3003. doi: 10.3390/nu16173003. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275318 Free PMC article.
-
Angina in 2022: Current Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 22;11(23):6891. doi: 10.3390/jcm11236891. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Metabolism in Cardiovascular Disease: Physiology, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Targets.Circ Res. 2023 Feb 3;132(3):379-396. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321667. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 36730380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ahf-Caltide, a Novel Polypeptide Derived from Calpastatin, Protects against Oxidative Stress Injury by Stabilizing the Expression of CaV1.2 Calcium Channel.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 29;24(21):15729. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115729. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958713 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of necroptosis-related diagnostic biomarkers in coronary heart disease.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 25;10(9):e30269. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30269. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

