3D In Vitro Platform for Cell and Explant Culture in Liquid-like Solids
- PMID: 35326418
- PMCID: PMC8946834
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11060967
3D In Vitro Platform for Cell and Explant Culture in Liquid-like Solids
Abstract
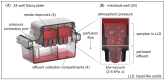
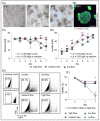
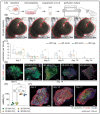
Existing 3D cell models and technologies have offered tools to elevate cell culture to a more physiologically relevant dimension. One mechanism to maintain cells cultured in 3D is by means of perfusion. However, existing perfusion technologies for cell culture require complex electronic components, intricate tubing networks, or specific laboratory protocols for each application. We have developed a cell culture platform that simply employs a pump-free suction device to enable controlled perfusion of cell culture media through a bed of granular microgels and removal of cell-secreted metabolic waste. We demonstrated the versatile application of the platform by culturing single cells and keeping tissue microexplants viable for an extended period. The human cardiomyocyte AC16 cell line cultured in our platform revealed rapid cellular spheroid formation after 48 h and ~90% viability by day 7. Notably, we were able to culture gut microexplants for more than 2 weeks as demonstrated by immunofluorescent viability assay and prolonged contractility.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; in vitro; liquid-like solids; microexplants; microgels; perfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design and fabrication of a liver-on-a-chip platform for convenient, highly efficient, and safe in situ perfusion culture of 3D hepatic spheroids.Lab Chip. 2018 Aug 21;18(17):2547-2562. doi: 10.1039/c8lc00333e. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 30019731
-
A 3D printed microfluidic perfusion device for multicellular spheroid cultures.Biofabrication. 2017 Sep 11;9(4):045005. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/aa8858. Biofabrication. 2017. PMID: 28837043
-
A pump-free microfluidic 3D perfusion platform for the efficient differentiation of human hepatocyte-like cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017 Oct;114(10):2360-2370. doi: 10.1002/bit.26341. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017. PMID: 28542705
-
Cell spheroids as a versatile research platform: formation mechanisms, high throughput production, characterization and applications.Biofabrication. 2021 Apr 8;13(3). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/abe6f2. Biofabrication. 2021. PMID: 33592595 Review.
-
Application of Three-dimensional (3D) Tumor Cell Culture Systems and Mechanism of Drug Resistance.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(34):3599-3607. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191014163923. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31612821 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryopreservation of human lung tissue for 3D ex vivo analysis.Respir Res. 2025 May 15;26(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03265-y. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40375251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-immune metaphenotypes orchestrate an evolutionary bottleneck that promotes metabolic transformation.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1323319. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323319. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38426105 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Confinement on the Dynamics of Normal and Tumor-Derived Pancreatic Ductal Organoids.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Dec 16;7(12):8489-8502. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01301. Epub 2024 Nov 22. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 39576883 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Bioconjugated Liquid-Like Solid (LLS) Enhance Characterization of Solid Tumor - Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 21:2023.02.17.529033. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.17.529033. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Acta Biomater. 2023 Dec;172:466-479. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.09.042. PMID: 36865164 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CAR T Cell Locomotion in Solid Tumor Microenvironment.Cells. 2022 Jun 20;11(12):1974. doi: 10.3390/cells11121974. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clevers H., Tuveson D.A. Organoid models for cancer research. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2019;3:223–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055702. - DOI
-
- Powley I.R., Patel M., Miles G., Pringle H., Howells L., Thomas A., Kettleborough C., Bryans J., Hammonds T., Macfarlane M., et al. Patient-derived explants (PDEs) as a powerful preclinical platform for anti-cancer drug and biomarker discovery. Br. J. Cancer. 2020;122:735–744. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0672-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaczmarczyk J.A., Roberts R.R., Luke B.T., Chan K.C., Van Wagoner C.M., Felder R.A., Saul R.G., Simona C., Blonder J. Comparative microsomal proteomics of a model lung cancer cell line NCI-H23 reveals distinct differences between molecular profiles of 3D and 2D cultured cells. Oncotarget. 2021;12:2022–2038. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

