Pre-Conditioning with IFN-γ and Hypoxia Enhances the Angiogenic Potential of iPSC-Derived MSC Secretome
- PMID: 35326438
- PMCID: PMC8946902
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11060988
Pre-Conditioning with IFN-γ and Hypoxia Enhances the Angiogenic Potential of iPSC-Derived MSC Secretome
Abstract
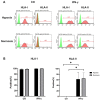
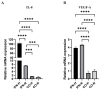
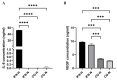
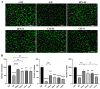
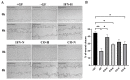
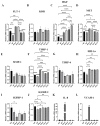
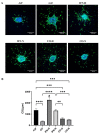
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs) represent a promising source of progenitor cells for approaches in the field of bone regeneration. Bone formation is a multi-step process in which osteogenesis and angiogenesis are both involved. Many reports show that the secretome of mesenchymal stromal stem cells (MSCs) influences the microenvironment upon injury, promoting cytoprotection, angiogenesis, and tissue repair of the damaged area. However, the effects of iPSC-derived MSCs secretome on angiogenesis have seldom been investigated. In the present study, the angiogenic properties of IFN-γ pre-conditioned iMSC secretomes were analyzed. We detected a higher expression of the pro-angiogenic genes and proteins of iMSCs and their secretome under IFN-γ and hypoxic stimulation (IFN-H). Tube formation and wound healing assays revealed a higher angiogenic potential of HUVECs in the presence of IFN-γ conditioned iMSC secretome. Sprouting assays demonstrated that within Coll/HA scaffolds, HUVECs spheroids formed significantly more and longer sprouts in the presence of IFN-γ conditioned iMSC secretome. Through gene expression analyses, pro-angiogenic genes (FLT-1, KDR, MET, TIMP-1, HIF-1α, IL-8, and VCAM-1) in HUVECs showed a significant up-regulation and down-regulation of two anti-angiogenic genes (TIMP-4 and IGFBP-1) compared to the data obtained in the other groups. Our results demonstrate that the iMSC secretome, pre-conditioned under inflammatory and hypoxic conditions, induced the highest angiogenic properties of HUVECs. We conclude that pre-activated iMSCs enhance their efficacy and represent a suitable cell source for collagen/hydroxyapatite with angiogenic properties.
Keywords: IFN-γ; angiogenesis; hypoxia; iMSC secretome; iPSC-derived MSCs; potentiation of iMSC efficacy; pre-conditioning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Secretome from iPSC-derived MSCs exerts proangiogenic and immunosuppressive effects to alleviate radiation-induced vascular endothelial cell damage.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jul 29;15(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03847-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39075600 Free PMC article.
-
Human iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) from aged individuals acquire a rejuvenation signature.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Mar 18;10(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1209-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30885246 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned medium from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 20;12(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02366-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34016178 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Conditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Regeneration Application.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Oct;28(5):966-977. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2021.0145. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022. PMID: 34569290 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs): A Promising Tool for Cell-Based Angiogenic Therapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2021;21(5):382-405. doi: 10.2174/1566523221666210917114353. Curr Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 34533444 Review.
Cited by
-
TNF-α Preconditioning Promotes a Proangiogenic Phenotype in hiPSC-Derived Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023 Apr 8;16(3):231-240. doi: 10.1007/s12195-023-00764-0. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 37456784 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironmental Modulation for Therapeutic Efficacy of Extracellular Vesicles.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(18):e2503027. doi: 10.1002/advs.202503027. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40145773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Tumor Angiogenesis for Therapeutic Advancements: Mechanistic Insights.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 9;12(4):827. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040827. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretome Derived from Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: A Promising Strategy for Diabetes and its Complications.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(10):1328-1350. doi: 10.2174/1574888X19666230913154544. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 37711134 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell secretome for regenerative medicine: Where do we stand?J Adv Res. 2025 Apr;70:103-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.004. Epub 2024 May 9. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38729561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

