Changes in miR-124-1, miR-212, miR-132, miR-134, and miR-155 Expression Patterns after 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene Treatment in CBA/Ca Mice
- PMID: 35326471
- PMCID: PMC8947631
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11061020
Changes in miR-124-1, miR-212, miR-132, miR-134, and miR-155 Expression Patterns after 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene Treatment in CBA/Ca Mice
Abstract
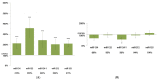
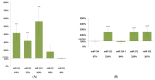
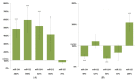
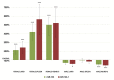
Specific gene and miRNA expression patterns are potential early biomarkers of harmful environmental carcinogen exposures. The aim of our research was to develop an assay panel by using several miRNAs for the rapid screening of potential carcinogens. The expression changes of miR-124-1, miR-212, miR-132, miR-134, and miR-155 were examined in the spleen, liver, and kidneys of CBA/Ca mice, following the 20 mg/bwkg intraperitoneal 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) treatment. After 24 h RNA was isolated, the miRNA expressions were analyzed by a real-time polymerase chain reaction and compared to a non-treated control. DMBA induced significant changes in the expression of miR-134, miR-132, and miR-124-1 in all examined organs in female mice. Thus, miR-134, miR-132, and miR-124-1 were found to be suitable biomarkers for the rapid screening of potential chemical carcinogens and presumably to monitor the protective effects of chemopreventive agents.
Keywords: 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene; carcinogen; miR-124-1; miR-132; miR-134; miR-155; miR-212; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Chemopreventive Effects of Polyphenols and Coffee, Based upon a DMBA Mouse Model with microRNA and mTOR Gene Expression Biomarkers.Cells. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):1300. doi: 10.3390/cells11081300. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455979 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 7,12-Dimethylbenz(α)anthracene on the Expression of miR-330, miR-29a, miR-9-1, miR-9-3 and the mTORC1 Gene in CBA/Ca Mice.In Vivo. 2020 Sep-Oct;34(5):2337-2343. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12046. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32871758 Free PMC article.
-
DMBA induces deregulation of miRNA expression of let-7, miR-21 and miR-146a in CBA/CA mice.In Vivo. 2012 Jan-Feb;26(1):113-7. In Vivo. 2012. PMID: 22210724
-
Very early effect of DMBA and MNU on microRNA expression.In Vivo. 2013 Jan-Feb;27(1):113-7. In Vivo. 2013. PMID: 23239859
-
Effect of E-2-(4'-methoxybenzylidene)-1-benzosuberone on the 7,12-dimethylbenz[alpha]anthracene-induced onco/suppressor gene action in vivo II: A 48-hour experiment.Anticancer Res. 2000 May-Jun;20(3A):1839-48. Anticancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10928116
Cited by
-
Construction of an Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration Diagnostic and Therapeutic Molecular Network Using Multi-Layer Network Analysis, a Fuzzy Logic Model, and Deep Learning Techniques: Are Retinal and Brain Neurodegenerative Disorders Related?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1555. doi: 10.3390/ph16111555. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004422 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemopreventive Effects of Polyphenols and Coffee, Based upon a DMBA Mouse Model with microRNA and mTOR Gene Expression Biomarkers.Cells. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):1300. doi: 10.3390/cells11081300. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455979 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation and Epigenetic Events Underlying Renal Cell Carcinomas.Cureus. 2022 Oct 27;14(10):e30743. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30743. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36447689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering novel therapeutic targets in glucose, nucleotides and lipids metabolism during cancer and neurological diseases.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241250293. doi: 10.1177/03946320241250293. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38712748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fruit Extract, Rich in Polyphenols and Flavonoids, Modifies the Expression of DNMT and HDAC Genes Involved in Epigenetic Processes.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 13;15(8):1867. doi: 10.3390/nu15081867. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danaei G., Vander Hoorn S., Lopez A.D., Murray C.J., Ezzati M. Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group (Cancers). Causes of cancer in the world: Comparative risk assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors. Lancet. 2005;366:1784–1793. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67725-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

