The Role of Catecholamines in Pathophysiological Liver Processes
- PMID: 35326472
- PMCID: PMC8947265
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11061021
The Role of Catecholamines in Pathophysiological Liver Processes
Abstract
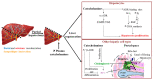
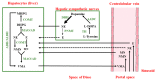
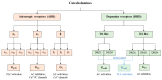
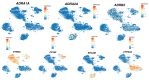
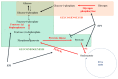
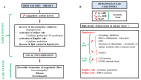
Over the last few years, the number of research publications about the role of catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine) in the development of liver diseases such as liver fibrosis, fatty liver diseases, or liver cancers is constantly increasing. However, the mechanisms involved in these effects are not well understood. In this review, we first recapitulate the way the liver is in contact with catecholamines and consider liver implications in their metabolism. A focus on the expression of the adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors by the liver cells is also discussed. Involvement of catecholamines in physiological (glucose metabolism, lipids metabolism, and liver regeneration) and pathophysiological (impact on drug-metabolizing enzymes expression, liver dysfunction during sepsis, fibrosis development, or liver fatty diseases and liver cancers) processes are then discussed. This review highlights the importance of understanding the mechanisms through which catecholamines influence liver functions in order to draw benefit from the adrenergic and dopaminergic antagonists currently marketed. Indeed, as these molecules are well-known drugs, their use as therapies or adjuvant treatments in several liver diseases could be facilitated.
Keywords: dopamine; epinephrine; hepatic cells; norepinephrine; sympathetic innervation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adori C., Daraio T., Kuiper R., Barde S., Horvathova L., Yoshitake T., Ihnatko R., Valladolid-Acebes I., Vercruysse P., Wellendorf A.M., et al. Disorganization and Degeneration of Liver Sympathetic Innervations in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Revealed by 3D Imaging. Sci. Adv. 2021;7:eabg5733. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg5733. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

