Prediction of Short and Long Survival after Surgery for Breast Cancer Brain Metastases
- PMID: 35326590
- PMCID: PMC8946189
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061437
Prediction of Short and Long Survival after Surgery for Breast Cancer Brain Metastases
Abstract
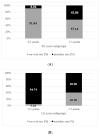
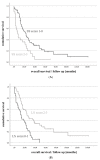
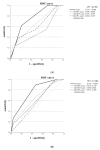
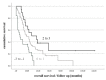
Background: Brain metastases requiring surgical treatment determine the prognosis of patients with breast cancer. We aimed to develop the scores for the prediction of short (<6 months) and long (≥3 years) survival after BCBM surgery. Methods: Female patients with BCBM surgery between 2008 and 2019 were included. The new scores were constructed upon independent predictors for short and long postoperative survival. Results: In the final cohort (n = 95), 18 (18.9%) and 22 (23.2%) patients experienced short and long postoperative survival, respectively. Breast-preserving surgery, presence of multiple brain metastases and age ≥ 65 years at breast cancer diagnosis were identified as independent predictors of short postoperative survival. In turn, positive HER2 receptor status in brain metastases, time interval ≥ 3 years between breast cancer and brain metastases diagnosis and KPS ≥ 90% independently predicted long survival. The appropriate short and long survival scores showed higher diagnostic accuracy for the prediction of short (AUC = 0.773) and long (AUC = 0.775) survival than the breast Graded Prognostic Assessment score (AUC = 0.498/0.615). A cumulative survival score (total score) showed significant association with overall survival (p = 0.001). Conclusion: We identified predictors independently impacting the prognosis after BCBM surgery. After external validation, the presented scores might become useful tools for the selection of proper candidates for BCBM surgery.
Keywords: HER2; brain metastasis; breast cancer; score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breast cancer with brain metastases: clinicopathologic features, survival, and paired biomarker analysis.Oncologist. 2015 May;20(5):466-73. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0107. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 25802405 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Brain Metastasis-Free Interval in Patients with Breast Cancer Brain Metastases.World Neurosurg. 2019 Aug;128:e157-e164. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.072. Epub 2019 Apr 26. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31035019
-
Analysis of Prognostic Factors Affecting the Brain Metastases Free Survival and Survival After Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 3;10:431. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00431. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32309214 Free PMC article.
-
Management of breast cancer brain metastases: Focus on human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2017 Mar 8;3(1):21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2017.01.004. eCollection 2017 Mar 25. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29063053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment strategies for breast cancer brain metastases.Br J Cancer. 2021 Jan;124(1):142-155. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01175-y. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33250512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breast Cancer Brain Metastases: A Neurosurgical Point of View From a Single-Center Experience.Cureus. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):e82306. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82306. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40376375 Free PMC article.
-
Development of graded prognostic assessment for breast Cancer brain metastasis incorporating extracranial metastatic features: a retrospective analysis of 284 patients.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 10;24(1):1262. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12983-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39390441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. Erratum in CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 313. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

