18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT for Early Prediction of Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas and EGFR Mutations Treated with First-Line EGFR-TKIs
- PMID: 35326662
- PMCID: PMC8945925
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061507
18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT for Early Prediction of Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas and EGFR Mutations Treated with First-Line EGFR-TKIs
Abstract
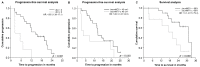
This study aims to investigate the role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) in early prediction of response and survival following epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas and EGFR mutations. Thirty patients with stage IIIB/IV lung adenocarcinomas and EGFR mutations receiving first-line EGFR-TKIs were prospectively evaluated between November 2012 and May 2015. EGFR mutations were quantified by delta cycle threshold (dCt). 18F-FDG PET/CT was performed before and 2 weeks after treatment initiation. PET response was assessed based on PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors (PERCIST). Baseline and percentage changes in the summed standardized uptake value, metabolic tumor volume (bsumMTV and ΔsumMTV, respectively), and total lesion glycolysis of ≤5 target lesions/patient were calculated. The association between parameters (clinical and PET) and non-progression disease after 3 months of treatment in CT based on the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors Version 1.1 (nPD3mo), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were tested. The median follow-up time was 19.6 months. The median PFS and OS were 12.0 and 25.3 months, respectively. The PERCIST criteria was an independent predictor of nPD3mo (p = 0.009), dCt (p = 0.014) and bsumMTV (p = 0.014) were independent predictors of PFS, and dCt (p = 0.014) and ΔsumMTV (p = 0.005) were independent predictors of OS. 18F-FDG PET/CT achieved early prediction of outcomes in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas and EGFR mutations receiving EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET; adenocarcinoma of lung; early response evaluation; survival; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Can 3'-deoxy-3'-(18)F-fluorothymidine or 2'-deoxy-2'-(18)F-fluoro-d-glucose PET/CT better assess response after 3-weeks treatment by epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, in non-small lung cancer patients? Preliminary results.Hell J Nucl Med. 2014 May-Aug;17(2):90-6. doi: 10.1967/s002449910136. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Hell J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24997081 Clinical Trial.
-
Standardized uptake value on (18)F-FDG-PET/CT is a predictor of EGFR T790M mutation status in patients with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs.Lung Cancer. 2016 Oct;100:14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.07.022. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27597275
-
Prognostic Value of Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT Functional Parameters in Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Stratified by EGFR Mutation Status.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 23;11(6):e0158307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158307. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27336755 Free PMC article.
-
The utility of 68F-FDG PET/CT for evaluation of tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Hell J Nucl Med. 2021 Sep-Dec;24(3):186-198. doi: 10.1967/s002449912402. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Hell J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 34901959
-
FDG-PET/CT response evaluation during EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with NSCLC.World J Radiol. 2014 Jul 28;6(7):392-8. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.392. World J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25071879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Research Progress of Anti-lung Cancer Drug-related Interstitial Lung Disease].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025 Apr 20;28(4):309-318. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.106.11. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40404479 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The role of artificial intelligence based on PET/CT radiomics in NSCLC: Disease management, opportunities, and challenges.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;13:1133164. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1133164. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36959810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and functional imaging in cancer-targeted therapy: current applications and future directions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Feb 27;8(1):89. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01366-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36849435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arteaga C.L. The epidermal growth factor receptor: From mutant oncogene in nonhuman cancers to therapeutic target in human neoplasia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001;19:32s–40s. - PubMed
-
- Wakeling A.E., Guy S.P., Woodburn J.R., Ashton S.E., Curry B.J., Barker A.J., Gibson K.H. ZD1839 (Iressa): An orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5749–5754. - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F., Caputo R., Bianco R., Damiano V., Pomatico G., Placido S.D., Bianco A.R., Tortora G. Antitumor effect and potentiation of cytotoxic drugs activity in human cancer cells by ZD-1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000;6:2053–2063. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

