In Vivo and In Vitro Enhanced Tumoricidal Effects of Metformin, Active Vitamin D3, and 5-Fluorouracil Triple Therapy against Colon Cancer by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR Network
- PMID: 35326689
- PMCID: PMC8946120
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061538
In Vivo and In Vitro Enhanced Tumoricidal Effects of Metformin, Active Vitamin D3, and 5-Fluorouracil Triple Therapy against Colon Cancer by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR Network
Abstract
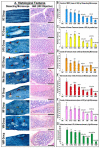
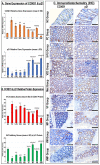
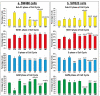
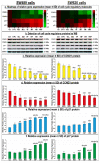
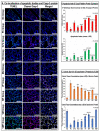
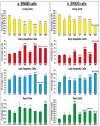
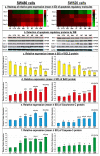
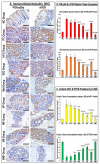
Chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is common during colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. This study measured the chemotherapeutic effects of 5-FU, active vitamin D3 (VD3), and/or metformin single/dual/triple regimens as complementary/alternative therapies. Ninety male mice were divided into: negative and positive (PC) controls, and 5-FU, VD3, Met, 5-FU/VD3, 5-FU/Met, VD3/Met, and 5-FU/VD3/Met groups. Treatments lasted four weeks following CRC induction by azoxymethane. Similar regimens were also applied in the SW480 and SW620 CRC cell lines. The PC mice had abundant tumours, markedly elevated proliferation markers (survivin/CCND1) and PI3K/Akt/mTOR, and reduced p21/PTEN/cytochrome C/caspase-3 and apoptosis. All therapies reduced tumour numbers, with 5-FU/VD3/Met being the most efficacious regimen. All protocols decreased cell proliferation markers, inhibited PI3K/Akt/mTOR molecules, and increased proapoptotic molecules with an apoptosis index, and 5-FU/VD3/Met revealed the strongest effects. In vitro, all therapies equally induced G1 phase arrest in SW480 cells, whereas metformin-alone showed maximal SW620 cell numbers in the G0/G1 phase. 5-FU/Met co-therapy also showed the highest apoptotic SW480 cell numbers (13%), whilst 5-FU/VD3/Met disclosed the lowest viable SW620 cell percentages (81%). Moreover, 5-FU/VD3/Met revealed maximal inhibitions of cell cycle inducers (CCND1/CCND3), cell survival (BCL2), and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR molecules alongside the highest expression of cell cycle inhibitors (p21/p27), proapoptotic markers (BAX/cytochrome C/caspase-3), and PTEN in both cell lines. In conclusion, metformin monotherapy was superior to VD3, whereas the 5-FU/Met protocol showed better anticancer effects relative to the other dual therapies. However, the 5-FU/VD3/Met approach displayed the best in vivo and in vitro tumoricidal effects related to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, justifiably by enhanced modulations of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis; calcitriol; cell cycle; chemoresistance; mammalian target of rapamycin; metformin; phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; protein kinase B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced in vitro tumoricidal effects of 5-Fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and active vitamin D3 triple therapy against colon cancer cells by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Life Sci. 2022 May 1;296:120442. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120442. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35245520
-
Metformin and thymoquinone co-treatment enhance 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity by suppressing the PI3K/mTOR/HIF1α pathway and increasing oxidative stress in colon cancer cells.Biofactors. 2023 Jul-Aug;49(4):831-848. doi: 10.1002/biof.1947. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Biofactors. 2023. PMID: 36929658
-
Exploring potential additive effects of 5-fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and coenzyme Q10 triple therapy on colon cancer cells in relation to glycolysis and redox status modulation.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2025 Mar 10;37(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s43046-025-00261-7. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2025. PMID: 40059278
-
Chemopreventive effects of vitamin D3 and its analogue, paricalcitol, in combination with 5-fluorouracil against colorectal cancer: The role of calcium signalling molecules.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Mar 1;1867(3):166040. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.166040. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33338596
-
Enhanced anti-cancer effects of oestrogen and progesterone co-therapy against colorectal cancer in males.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 3;13:941834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.941834. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36263327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Anticancer and Antibacterial Activities of the Essential Oil of Forsskal's Basil Growing in Extreme Environmental Conditions.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 26;13(3):651. doi: 10.3390/life13030651. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983807 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of Metformin to Improve Survival Outcomes in Patients With Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70567. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70567. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39757744 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin exerts an antitumor effect by inhibiting bladder cancer cell migration and growth, and promoting apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.BMC Urol. 2022 May 24;22(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01027-2. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 35610639 Free PMC article.
-
Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in Combination with 5-FU Exert Antitumor Effects Superior to Those of the Active Drug in a Colon Cancer Cell Model.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 11;15(1):245. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010245. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678874 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Effects and Mechanisms of Metabolic Syndrome Medications on Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Dec 14;9:1279-1298. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S392051. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 36545268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

