Metabolic Profiling of Thymic Epithelial Tumors Hints to a Strong Warburg Effect, Glutaminolysis and Precarious Redox Homeostasis as Potential Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 35326714
- PMCID: PMC8945961
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061564
Metabolic Profiling of Thymic Epithelial Tumors Hints to a Strong Warburg Effect, Glutaminolysis and Precarious Redox Homeostasis as Potential Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
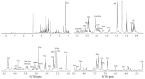
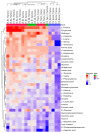
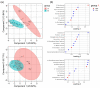
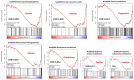
Thymomas and thymic carcinomas (TC) are malignant thymic epithelial tumors (TETs) with poor outcome, if non-resectable. Metabolic signatures of TETs have not yet been studied and may offer new therapeutic options. Metabolic profiles of snap-frozen thymomas (WHO types A, AB, B1, B2, B3, n = 12) and TCs (n = 3) were determined by high resolution magic angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (HRMAS 1H-NMR) spectroscopy. Metabolite-based prediction of active KEGG metabolic pathways was achieved with MetPA. In relation to metabolite-based metabolic pathways, gene expression signatures of TETs (n = 115) were investigated in the public "The Cancer Genome Atlas" (TCGA) dataset using gene set enrichment analysis. Overall, thirty-seven metabolites were quantified in TETs, including acetylcholine that was not previously detected in other non-endocrine cancers. Metabolite-based cluster analysis distinguished clinically indolent (A, AB, B1) and aggressive TETs (B2, B3, TCs). Using MetPA, six KEGG metabolic pathways were predicted to be activated, including proline/arginine, glycolysis and glutathione pathways. The activated pathways as predicted by metabolite-profiling were generally enriched transcriptionally in the independent TCGA dataset. Shared high lactic acid and glutamine levels, together with associated gene expression signatures suggested a strong "Warburg effect", glutaminolysis and redox homeostasis as potential vulnerabilities that need validation in a large, independent cohort of aggressive TETs. If confirmed, targeting metabolic pathways may eventually prove as adjunct therapeutic options in TETs, since the metabolic features identified here are known to confer resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy, kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint blockers, i.e., currently used therapies for non-resectable TETs.
Keywords: HRMAS 1H-NMR; biomarker; metabolomics; thymic carcinoma; thymoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest in terms of the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Marx A., Chan J.K.C., Chalabreysse L., Dacic S., Detterbeck F., French C.A., Hornick J.L., Inagaki H., Jain D., Lazar A.J., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Thymus and Mediastinum: What Is New in Thymic Epithelial, Germ Cell, and Mesenchymal Tumors? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021;17:200–213. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.10.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Belharazem D., Grass A., Paul C., Vitacolonna M., Schalke B., Rieker R.J., Körner D., Jungebluth P., Simon-Keller K., Hohenberger P., et al. Increased cFLIP expression in thymic epithelial tumors blocks autophagy via NF-κB signalling. Oncotarget. 2017;8:89580–89594. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15929. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y., Weis C.-A., Thelen J., Sticht C., Schalke B., Ströbel P., Marx A. Thymoma Associated Myasthenia Gravis (TAMG): Differential Expression of Functional Pathways in Relation to MG Status in Different Thymoma Histotypes. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00664. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

