Regulation of a Novel Splice Variant of Early Growth Response 4 (EGR4-S) by HER+ Signalling and HSF1 in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35326716
- PMCID: PMC8946690
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061567
Regulation of a Novel Splice Variant of Early Growth Response 4 (EGR4-S) by HER+ Signalling and HSF1 in Breast Cancer
Abstract
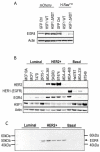
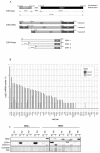
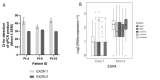
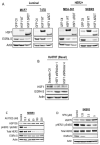
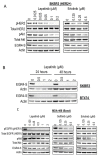
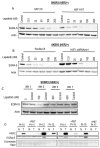
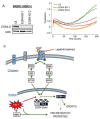
The zinc finger transcription factor EGR4 has previously been identified as having a critical role in the proliferation of small cell lung cancer. Here, we have identified a novel, shortened splice variant of this transcription factor (EGR4-S) that is regulated by Heat Shock Factor-1 (HSF1). Our findings demonstrate that the shortened variant (EGR4-S) is upregulated with high EGFR, HER2, and H-Rasv12-expressing breast cell lines, and its expression is inhibited in response to HER pathway inhibitors. Protein and mRNA analyses of HER2+ human breast tumours indicated the novel EGR4-S splice variant to be preferentially expressed in tumour tissue and not detectable in patient-matched normal tissue. Knockdown of EGR4-S in the HER2-amplified breast cancer cell line SKBR3 reduced cell growth, suggesting that EGR4-S supports the growth of HER2+ tumour cells. In addition to chemical inhibitors of the HER2 pathway, EGR4-S expression was also found to be suppressed by chemical stressors and the overexpression of HSF1. Under these conditions, reduced EGR4-S levels were associated with the observed lower cell growth rate, but the augmentation of properties associated with higher metastatic potential. Taken together, these findings identify EGR4-S as a potential biomarker for HER2 pathway activation in human tumours that is regulated by HSF1.
Keywords: EGR4; HER2; HSF1; breast cancer; molecular stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early growth response 4 is involved in cell proliferation of small cell lung cancer through transcriptional activation of its downstream genes.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 20;9(11):e113606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113606. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25411851 Free PMC article.
-
HER2/ErbB2 activates HSF1 and thereby controls HSP90 clients including MIF in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 2;5(1):e980. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.508. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24384723 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of EGR4 as a prospective target for inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and a novel biomarker in colorectal cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Jun;31(6):871-883. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00743-1. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38459370
-
A positive feedback loop between ZNF205-AS1 and EGR4 promotes non-small cell lung cancer growth.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):1495-1508. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14056. Epub 2018 Dec 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30556283 Free PMC article.
-
Gramicidin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by suppressing EGR4.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;48(1):53-59. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1699808. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31852273
Cited by
-
Joint Screening for Ultra-High Dimensional Multi-Omics Data.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;11(12):1193. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11121193. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768011 Free PMC article.
-
NFYA-mediated promotion of castration-resistant prostate cancer progression through EGR4 regulation.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 5;15(1):528. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01392-4. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39367986 Free PMC article.
-
Early Growth Response Factor 4 (EGR4) Expression in Gut Tissues and Regional Lymph Nodes of Cattle with Different Types of Paratuberculosis-Associated Lesions: Potential Role of EGR4 in Resilience to Paratuberculosis.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;15(7):1012. doi: 10.3390/ani15071012. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218405 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

