Circadian and Immunity Cycle Talk in Cancer Destination: From Biological Aspects to In Silico Analysis
- PMID: 35326729
- PMCID: PMC8945968
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14061578
Circadian and Immunity Cycle Talk in Cancer Destination: From Biological Aspects to In Silico Analysis
Abstract
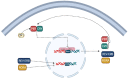
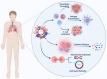
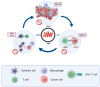
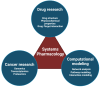
Cancer is the leading cause of death and a major problem to increasing life expectancy worldwide. In recent years, various approaches such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapies, and the newest pillar, immunotherapy, have been developed to treat cancer. Among key factors impacting the effectiveness of treatment, the administration of drugs based on the circadian rhythm in a person and within individuals can significantly elevate drug efficacy, reduce adverse effects, and prevent drug resistance. Circadian clocks also affect various physiological processes such as the sleep cycle, body temperature cycle, digestive and cardiovascular processes, and endocrine and immune systems. In recent years, to achieve precision patterns for drug administration using computational methods, the interaction of the effects of drugs and their cellular pathways has been considered more seriously. Integrated data-derived pathological images and genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics analyses have provided an understanding of the molecular basis of cancer and dramatically revealed interactions between circadian and immunity cycles. Here, we describe crosstalk between the circadian cycle signaling pathway and immunity cycle in cancer and discuss how tumor microenvironment affects the influence on treatment process based on individuals' genetic differences. Moreover, we highlight recent advances in computational modeling that pave the way for personalized immune chronotherapy.
Keywords: cancer immunity cycle; circadian cycle; computational biology; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circadian clock: a regulator of the immunity in cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Mar 22;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00721-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33752691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronopharmacological strategies focused on chrono-drug discovery.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Oct;202:72-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31173839 Review.
-
The circadian timing system in clinical oncology.Ann Med. 2014 Jun;46(4):191-207. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2014.916990. Ann Med. 2014. PMID: 24915535 Review.
-
Spotlight on Circadian Genes and Colorectal Cancer Crosstalk.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(1):4-11. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200624192517. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 32579510 Review.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-219 in the central nervous system: a potential theranostic approach.Res Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec 15;19(6):634-655. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_163_23. eCollection 2024 Dec. Res Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39911893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian lifestyle determinants of immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 4;13:1284089. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1284089. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38111535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy around the Clock: Impact of Infusion Timing on Stage IV Melanoma Outcomes.Cells. 2023 Aug 15;12(16):2068. doi: 10.3390/cells12162068. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626878 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Circadian Rhythm and Cancer Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115846. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The circadian rhythm: an influential soundtrack in the diabetes story.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 27;14:1156757. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1156757. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37441501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qian D.C., Kleber T., Brammer B., Xu K.M., Switchenko J.M., Janopaul-Naylor J.R., Zhong J., Yushak M.L., Harvey R.D., Paulos C.M., et al. Effect of immunotherapy time-of-day infusion on overall survival among patients with advanced melanoma in the USA (MEMOIR): A propensity score-matched analysis of a single-centre, longitudinal study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1777–1786. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00546-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

