Citrus bergamia: Kinetics of Antimicrobial Activity on Clinical Isolates
- PMID: 35326824
- PMCID: PMC8944555
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030361
Citrus bergamia: Kinetics of Antimicrobial Activity on Clinical Isolates
Abstract
Background: The inappropriate use of antibiotics has increased selective pressure and the spread of multi-drug-resistant (MDR) pathogens, which reduces the possibility of effective treatment. A potential alternative therapeutic approach may be represented by essential oils, such as the distilled extract of bergamot (Citrus bergamia Risso et Poiteau). Such natural products exercise numerous biological activities, including antimicrobial effects.
Methods: This work aimed to evaluate the kinetics of the bactericidal and fungicidal activity of the distilled extract of bergamot on MDR bacteria and fungi from clinical specimens using the time-kill assay. Furthermore, the antimicrobial activity of the distilled extract of bergamot on the morphology and cellular organization of clinical pathogens was evaluated by confocal laser scanning microscopy.
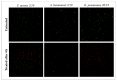
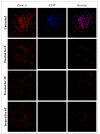
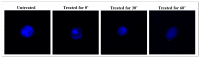
Results: Our results demonstrated that the distilled extract of bergamot exhibited significant antimicrobial activity and a specific bactericidal effect against the bacterial and fungal strains tested. Furthermore, confocal microscope images clearly showed compromised membrane integrity, damage and cell death in bacterial samples treated with the distilled extract of bergamot. In addition, progressive alterations in cell-wall composition, cytoplasmic material and nucleus structure triggered by exposure to the distilled extract of bergamot were identified in the fungal samples considered.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the use of essential oils, such as distilled extract of bergamot (Citrus bergamia Risso et Poiteau), can represent a valid alternative therapeutic strategy to counteract antibiotic resistance of pathogens.
Keywords: Citrus bergamia; antimicrobial activity; fungicidal activity; multi-drug-resistant bacteria; time-kill assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Glass Whole-Genome Sequencing for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. 2017. [(accessed on 21 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

