How COVID-19 Has Influenced Public Interest in Antimicrobials, Antimicrobial Resistance and Related Preventive Measures: A Google Trends Analysis of Italian Data
- PMID: 35326842
- PMCID: PMC8944652
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030379
How COVID-19 Has Influenced Public Interest in Antimicrobials, Antimicrobial Resistance and Related Preventive Measures: A Google Trends Analysis of Italian Data
Abstract
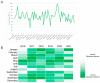
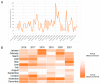
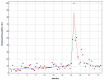
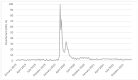
Google Trends analytics is an innovative way to evaluate public interest in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and related preventive measures. In the present study, we analyzed Google Trends data in Italy, from 2016 to 2021. A joinpoint analysis was performed to assess whether and how annual campaigns and the COVID-19 pandemic affected public interest in antimicrobials, AMR, hand hygiene, and the use of disinfectant. For the terms "antimicrobials" and "antimicrobial resistance", no joinpoints were detected around the time of the World Antimicrobial Awareness Week. Similarly, the COVID-19 pandemic seems to have had no effect on public interest in this term. For the term "handwashing", no joinpoints were detected around World Hand Hygiene Day or Global Handwashing Day. However, three joinpoints were detected around the peak of interest observed in March 2020, after the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Comparable results were obtained for the term "disinfectant". These findings show that the influence of annual campaigns on public interest in AMR and preventive measures was modest and not long-term. The COVID-19 pandemic, meanwhile, had no effect on AMR but raised awareness on preventive measures. However, this was a temporary rather than long-term outcome. Thus, different policies, strategies, and measures should be designed to advocate prevention of AMR in the COVID-19 era.
Keywords: Google analytics; antibiotic resistance; disinfectant; hand hygiene; handwashing; preventive measures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of the World Antimicrobial Awareness Week on public interest between 2015 and 2020: A Google Trends analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Oct;111:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.018. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34391908
-
Impact of the world hand hygiene and global handwashing days on public awareness between 2016 and 2020: Google trends analysis.Am J Infect Control. 2022 Feb;50(2):141-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2021.08.033. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Am J Infect Control. 2022. PMID: 34718066
-
Public awareness of preventive measures against COVID-19: an infodemiology study.Hong Kong Med J. 2023 Jun;29(3):214-223. doi: 10.12809/hkmj219556. Hong Kong Med J. 2023. PMID: 37349138
-
Flare of the silent pandemic in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic: Obstacles and opportunities.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Feb 26;11(6):1267-1274. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1267. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 36926133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
It is complicated: Potential short- and long-term impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on antimicrobial resistance-An expert review.Antimicrob Steward Healthc Epidemiol. 2022 Feb 18;2(1):e27. doi: 10.1017/ash.2022.10. eCollection 2022. Antimicrob Steward Healthc Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 36310817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial patterns and temporal trends in stillbirth, neonatal, and infant mortality: an exploration of country-level data from 2000 to 2021.J Glob Health. 2025 Feb 21;15:04034. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04034. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 39977670 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Global Interest in Propolis, Nanosilver, and Biomaterials: Insights and Implications for Dentistry from Big Data Analytics.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Jun 6;13(6):253. doi: 10.3390/dj13060253. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559156 Free PMC article.
-
How COVID-19 Pandemic Has Influenced Public Interest in Foods: A Google Trends Analysis of Italian Data.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 20;20(3):1976. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031976. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767342 Free PMC article.
-
Climate change and the global food chain: a catalyst for emerging infectious diseases?Int J Emerg Med. 2025 Aug 11;18(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12245-025-00901-8. Int J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40790563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Antimicrobial Resistance Is Linked to Climate Change: An Overview of Two Intertwined Global Challenges.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 17;20(3):1681. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031681. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ECDC Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2022–2020 Data. 2022. [(accessed on 1 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-resistance....
-
- WHO World Antimicrobial Awareness Week. [(accessed on 1 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/campaigns/world-antimicrobial-awareness-week.
-
- WHO World Hand Hygiene Day. [(accessed on 1 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/campaigns/world-hand-hygiene-day.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

