A Ternary Copper (II) Complex with 4-Fluorophenoxyacetic Acid Hydrazide in Combination with Antibiotics Exhibits Positive Synergistic Effect against Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 35326852
- PMCID: PMC8944508
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030388
A Ternary Copper (II) Complex with 4-Fluorophenoxyacetic Acid Hydrazide in Combination with Antibiotics Exhibits Positive Synergistic Effect against Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
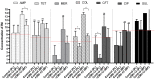
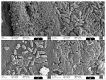
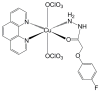
Salmonella spp. continues to figure prominently in world epidemiological registries as one of the leading causes of bacterial foodborne disease. We characterised 43 Brazilian lineages of Salmonella Typhimurium (ST) strains, characterized drug resistance patterns, tested copper (II) complex as control options, and proposed effective antimicrobial measures. The minimum inhibitory concentration was evaluated for seven antimicrobials, isolated and combined with the copper (II) complex [Cu(4-FH)(phen)(ClO4)2] (4-FH = 4-fluorophenoxyacetic acid hydrazide and phen = 1,10-phenanthroline), known as DRI-12, in planktonic and sessile ST. In parallel, 42 resistance genes were screened (PCR/microarray). All strains were multidrug resistant (MDR). Resistance to carbapenems and polymyxins (86 and 88%, respectively) have drawn attention to the emergence of the problem in Brazil, and resistance is observed also to CIP and CFT (42 and 67%, respectively), the drugs of choice in treatment. Resistance to beta-lactams was associated with the genes blaTEM/blaCTX-M in 39% of the strains. Lower concentrations of DRI-12 (62.7 mg/L, or 100 μM) controlled planktonic and sessile ST in relation to AMP/SUL/TET and AMP/SUL/TET/COL, respectively. The synergistic effect provided by DRI-12 was significant for COL/CFT and COL/AMP in planktonic and sessile ST, respectively, and represents promising alternatives for the control of MDR ST.
Keywords: food safety; multi drug resistance (MDR); salmonellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibiofilm Activity of β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combination against Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium.Pathogens. 2022 Mar 13;11(3):349. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11030349. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35335673 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of foodborne salmonellosis serotypes and drug resistance in children in Chenzhou City of China from 2017 through 2022.Transl Pediatr. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):921-930. doi: 10.21037/tp-24-120. Epub 2024 May 15. Transl Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38984026 Free PMC article.
-
Colistin-, cefepime-, and levofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from Egyptian chicken carcasses.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024 Jul 4;23(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00713-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024. PMID: 38965586 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance patterns in Salmonella Typhimurium and its monophasic variant from pigs in southern Spain.Res Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 20;152:596-603. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.09.028. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Res Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36201906
-
Antimicrobial resistance and resistance genes in Salmonella strains isolated from broiler chickens along the slaughtering process in China.Int J Food Microbiol. 2017 Oct 16;259:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Int J Food Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28800411
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Challenged with Platinum(II) and Palladium(II) Complexes Containing 1,10-Phenanthroline and 5-Amino-1,3,4-Thiadiazole-2(3H)-Thione in Campylobacter jejuni.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;11(11):1645. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111645. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421289 Free PMC article.
-
Interference with Bacterial Conjugation and Natural Alternatives to Antibiotics: Bridging a Gap.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;12(7):1127. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12071127. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508224 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for Special Issue "Antibacterial Resistance and Novel Strategies to Eradicate Bacterial Biofilms".Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 1;11(9):1184. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091184. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brasil Ministério da Agricultura, P. e A. Anuário dos Programas de Controle de Alimentos de Origem Animal do DIPOA. Secretaria de Defesa Agropecuária, Departamento de Inspeção de Produtos de Origem Animal, Coordenação Geral de Programas Especiais 2021, 7. [(accessed on 14 February 2022)]; Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-animal/a....
-
- WHO—World Health Organization Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal) [(accessed on 14 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal)
-
- USDA—United States Department of Agriculture FSIS Guideline for Controlling Salmonella in Raw Poultry. [(accessed on 14 January 2022)]; Available online: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media_file/2021-07/FSIS-GD....
-
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde Surtos de Doenças Transmitidas por Alimentos no Brasil 2022. [(accessed on 14 February 2022)]; Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-de-a-a-z/d/doencas-de-tran....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

