Evaluation of Bacteriophage-Antibiotic Combination Therapy for Biofilm-Embedded MDR Enterococcus faecium
- PMID: 35326855
- PMCID: PMC8944492
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030392
Evaluation of Bacteriophage-Antibiotic Combination Therapy for Biofilm-Embedded MDR Enterococcus faecium
Abstract
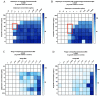
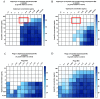
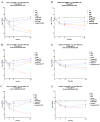
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Enterococcus faecium is a challenging pathogen known to cause biofilm-mediated infections with limited effective therapeutic options. Lytic bacteriophages target, infect, and lyse specific bacterial cells and have anti-biofilm activity, making them a possible treatment option. Here, we examine two biofilm-producing clinical E. faecium strains, daptomycin (DAP)-resistant R497 and DAP-susceptible dose-dependent (SDD) HOU503, with initial susceptibility to E. faecium bacteriophage 113 (ATCC 19950-B1). An initial synergy screening was performed with modified checkerboard MIC assays developed by our laboratory to efficiently screen for antibiotic and phage synergy, including at very low phage multiplicity of infection (MOI). The data were compared by one-way ANOVA and Tukey (HSD) tests. In 24 h time kill analyses (TKA), combinations with phage-DAP-ampicillin (AMP), phage-DAP-ceftaroline (CPT), and phage-DAP-ertapenem (ERT) were synergistic and bactericidal compared to any single agent (ANOVA range of mean differences 3.34 to 3.84 log10 CFU/mL; p < 0.001). Furthermore, phage-DAP-AMP and phage-DAP-CPT prevented the emergence of DAP and phage resistance. With HOU503, the combination of phage-DAP-AMP showed the best killing effect, followed closely by phage-DAP-CPT; both showed bactericidal and synergistic effects compared to any single agent (ANOVA range of mean differences 3.99 to 4.08 log10 CFU/mL; p < 0.001).
Keywords: Enterococcus faecium; antimicrobial; bacteriophage; biofilm; frequency of resistance; nontraditional antibacterial; phage sensitivity; phage therapy; resistance management.
Conflict of interest statement
K.L., A.J.K.C., R.K., T.M., K.C.S., D.J.H., G.S.C., C.A.A. and M.J.R. have nothing to declare. M.J.R. has received grant support from and has consulted or spoken on behalf of Allergan, Melinta, Merck, Paratek, Shionogi, Spero, and Tetraphase. C.A.A. has received grant support from Merck and MeMed Diagnostics, and is a co-founder of Entasis Therapeutics and shareholder in Ancilia Biosciences, C.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phage Cocktails with Daptomycin and Ampicillin Eradicates Biofilm-Embedded Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus faecium with Preserved Phage Susceptibility.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;11(9):1175. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091175. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139953 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-Antibiotic Cocktail Rescues Daptomycin and Phage Susceptibility against Daptomycin-Nonsusceptible Enterococcus faecium in a Simulated Endocardial Vegetation Ex Vivo Model.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0034023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00340-23. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37338375 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Daptomycin Dose Exposure Alone or in Combination with β-Lactams or Rifampin against Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in an In Vitro Biofilm Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Apr 21;64(5):e02074-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02074-19. Print 2020 Apr 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32094136 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage Therapy as a Promising Alternative for Antibiotic-Resistant Enterococcus faecium: Advances and Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;13(12):1120. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121120. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pre-clinical Impact of the Synergistic Mechanism of Daptomycin and Ceftaroline on Patients with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Infections.Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021;16(4):296-299. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666210108103813. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33423652 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting phage-antibiotic synergies to disrupt Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilms in the context of orthopedic infections.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0321923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03219-23. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38084971 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-antibiotic synergy against daptomycin-nonsusceptible MRSA in an ex vivo simulated endocardial pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Apr 3;68(4):e0138823. doi: 10.1128/aac.01388-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38376187 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic phage administration provides a time window for delayed treatment of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis in a murine bacteremia model.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 24;15:1504696. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1504696. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39925887 Free PMC article.
-
Phage Cocktails with Daptomycin and Ampicillin Eradicates Biofilm-Embedded Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus faecium with Preserved Phage Susceptibility.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;11(9):1175. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091175. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139953 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-Antibiotic Cocktail Rescues Daptomycin and Phage Susceptibility against Daptomycin-Nonsusceptible Enterococcus faecium in a Simulated Endocardial Vegetation Ex Vivo Model.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0034023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00340-23. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37338375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.) Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. [(accessed on 3 May 2021)];2019 Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/82532.
-
- Chiang H.-Y., Perencevich E.N., Nair R., Nelson R.E., Samore M., Khader K., Chorazy M.L., Herwaldt L.A., Blevins A., Ward M.A., et al. Incidence and Outcomes Associated with Infections Caused by Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in the United States: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017;38:203–215. doi: 10.1017/ice.2016.254. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

