The Effect of Tannin-Rich Witch Hazel on Growth of Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum
- PMID: 35326857
- PMCID: PMC8944479
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030395
The Effect of Tannin-Rich Witch Hazel on Growth of Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum
Abstract
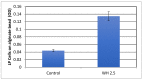
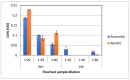
Probiotic bacteria help maintain microbiome homeostasis and promote gut health. Maintaining the competitive advantage of the probiotics over pathogenic bacteria is a challenge, as they are part of the gut microbiome that is continuously exposed to digestive and nutritional changes and various stressors. Witch hazel that is rich in hamamelitannin (WH, whISOBAXTM) is an inhibitor of growth and virulence of pathogenic bacteria. To test for its effect on probiotic bacteria, WH was tested on the growth and biofilm formation of a commercially available probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum PS128. As these bacteria are aerotolerant, the experiments were carried out aerobically and in nutritionally inadequate/poor (nutrient broth) or adequate/rich (MRS broth) conditions. Interestingly, despite its negative effect on the growth and biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus epidermidis, WH promotes the growth of the probiotic bacteria in a nutritionally inadequate environment while maintaining their growth under a nutritionally rich environment. In the absence of WH, no significant biofilm is formed on the surfaces tested (polystyrene and alginate), but in the presence of WH, biofilm formation was significantly enhanced. These results indicate that WH may thus be used to enhance the growth and survival of probiotics.
Keywords: Lactobacillus plantarum; biofilm; prebiotic; probiotic; witch hazel (Hamamelis).
Conflict of interest statement
N.B. holds shares in StaphOff Biotech Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a Witch Hazel Extract for the Potential Prebiotic and Protective Effect on Select Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (Prev. Lactobacillus plantarum) Strains.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 29;9:874666. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.874666. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35571953 Free PMC article.
-
Witch Hazel Significantly Improves the Efficacy of Commercially Available Teat Dips.Pathogens. 2020 Feb 1;9(2):92. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9020092. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32024049 Free PMC article.
-
whISOBAXTM Inhibits Bacterial Pathogenesis and Enhances the Effect of Antibiotics.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 May 19;9(5):264. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9050264. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32438609 Free PMC article.
-
Immunonutrition: role of biosurfactants, fiber, and probiotic bacteria.Nutrition. 1998 Jul-Aug;14(7-8):585-94. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(98)00030-6. Nutrition. 1998. PMID: 9684261 Review.
-
Roles of Probiotic Lactobacilli Inclusion in Helping Piglets Establish Healthy Intestinal Inter-environment for Pathogen Defense.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018 Jun;10(2):243-250. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9273-y. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018. PMID: 28361445 Review.
Cited by
-
Hamamelis virginiana L. in Skin Care: A Review of Its Pharmacological Properties and Cosmetological Applications.Molecules. 2025 Jun 26;30(13):2744. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132744. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nikolic D.M. Homeostatic Microbiome (Microbiota)—Formation, Maintenance and Influence on Human Health. [(accessed on 19 October 2021)];J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Res. 2018 7:2729–2733. Available online: http://www.ghrnet.org/index.php/joghr/article/view/2471.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

