Rational Use of Danofloxacin for Treatment of Mycoplasma gallisepticum in Chickens Based on the Clinical Breakpoint and Lung Microbiota Shift
- PMID: 35326865
- PMCID: PMC8944443
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030403
Rational Use of Danofloxacin for Treatment of Mycoplasma gallisepticum in Chickens Based on the Clinical Breakpoint and Lung Microbiota Shift
Abstract
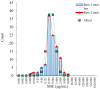
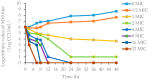
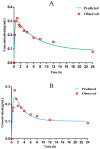
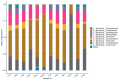
The study was to explore the rational use of danofloxacin against Mycoplasma gallisepticum (MG) based on its clinical breakpoint (CBP) and the effect on lung microbiota. The CBP was established according to epidemiological cutoff value (ECV/COWT), pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) cutoff value (COPD) and clinical cutoff value (COCL). The ECV was determined by the micro-broth dilution method and analyzed by ECOFFinder software. The COPD was determined according to PK-PD modeling of danofloxacin in infected lung tissue with Monte Carlo analysis. The COCL was performed based on the relationship between the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the possibility of cure (POC) from clinical trials. The CBP in infected lung tissue was 1 μg/mL according to CLSI M37-A3 decision tree. The 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequencing results showed that the lung microbiota, especially the phyla Firmicutes and Proteobacteria had changed significantly along with the process of cure regimen (the 24 h dosing interval of 16.60 mg/kg b.w for three consecutive days). Our study suggested that the rational use of danofloxacin for the treatment of MG infections should consider the MIC and effect of antibiotics on the respiratory microbiota.
Keywords: Mycoplasma gallisepticum; PK–PD cutoff values; clinical breakpoint; clinical cutoff values; danofloxacin; epidemiological cutoff values; lung microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prudent Use of Tylosin for Treatment of Mycoplasma gallisepticum Based on Its Clinical Breakpoint and Lung Microbiota Shift.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 9;12:712473. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.712473. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34566919 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Clinical Breakpoint of Danofloxacin for Glaesserella parasuis in Plasma and in PELF.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;10(7):808. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070808. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356730 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility breakpoint for Danofloxacin against swine Escherichia coli.BMC Vet Res. 2019 Feb 4;15(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1783-2. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 30717803 Free PMC article.
-
The PK-PD Relationship and Resistance Development of Danofloxacin against Mycoplasma gallisepticum in An In Vivo Infection Model.Front Microbiol. 2017 May 30;8:926. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00926. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28611739 Free PMC article.
-
How can we predict bacterial eradication?Int J Infect Dis. 2003 Mar;7 Suppl 1:S13-20. doi: 10.1016/s1201-9712(03)90066-x. Int J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12839703 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of Danofloxacin in Gushi Chickens after Single Oral and Intravenous Administration.Metabolites. 2023 Aug 2;13(8):906. doi: 10.3390/metabo13080906. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37623849 Free PMC article.
-
Halicin: A New Horizon in Antibacterial Therapy against Veterinary Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 27;13(6):492. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060492. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927159 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the complexities of poultry respiratory microbiota: colonization, composition, and impact on health.Anim Microbiome. 2024 May 6;6(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s42523-024-00308-5. Anim Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38711114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza a virus subtype H9N2 infection induces respiratory microbiota dysbiosis in chickens via type-I interferon-mediated mechanisms.FEMS Microbes. 2025 Feb 3;6:xtaf001. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtaf001. eCollection 2025. FEMS Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39991080 Free PMC article.
-
The analysis of antimicrobials epidemiological cut-off values of mycoplasma gallisepticum isolated from goose.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):104974. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104974. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40080949 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

