Orthopaedic Implant-Associated Staphylococcal Infections: A Critical Reappraisal of Unmet Clinical Needs Associated with the Implementation of the Best Antibiotic Choice
- PMID: 35326869
- PMCID: PMC8944676
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030406
Orthopaedic Implant-Associated Staphylococcal Infections: A Critical Reappraisal of Unmet Clinical Needs Associated with the Implementation of the Best Antibiotic Choice
Abstract
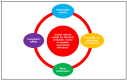
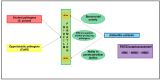
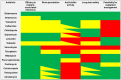
Infections associated with orthopaedic implants represent a major health concern characterized by a remarkable incidence of morbidity and mortality. The wide variety of clinical scenarios encountered in the heterogeneous world of infections associated with orthopaedic implants makes the implementation of an optimal and standardized antimicrobial treatment challenging. Antibiotic bone penetration, anti-biofilm activity, long-term safety, and drug choice/dosage regimens favouring outpatient management (i.e., long-acting or oral agents) play a major role in regards to the chronic evolution of these infections. The aim of this multidisciplinary opinion article is to summarize evidence supporting the use of the different anti-staphylococcal agents in terms of microbiological and pharmacological optimization according to bone penetration, anti-biofilm activity, long-term safety, and feasibility for outpatient regimens, and to provide a useful guide for clinicians in the management of patients affected by staphylococcal infections associated with orthopaedic implants Novel long-acting lipoglycopeptides, and particularly dalbavancin, alone or in combination with rifampicin, could represent the best antibiotic choice according to real-world evidence and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties. The implementation of a multidisciplinary taskforce and close cooperation between microbiologists and clinicians is crucial for providing the best care in this scenario.
Keywords: anti-staphylococcal agents; antibiotic bone penetration; biofilm; long-term safety; orthopaedic implant-associated infections; outpatient management.
Conflict of interest statement
M.G. received personal fees from Angelini; B.V. participated on advisory boards, in a speaker’s bureau, and received research contracts, contributions and study grants from Abbott, Accelerate Diagnostics, Ada, Alifax, Angelini, Becton, Dickinson and Company, Bellco Drug Corporation, bioMerieux, Inc., Biotest, Cepheid, Correvio, Gilead, Menarini, MSD Italia, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Shionogi Inc., and Thermo Fisher Scientific; A.G. received personal fees from Menarini and Medivis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-World Use of Dalbavancin in the Era of Empowerment of Outpatient Antimicrobial Treatment: A Careful Appraisal Beyond Approved Indications Focusing on Unmet Clinical Needs.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Aug 3;15:3349-3378. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S313756. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34376971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations for optimizing antimicrobial therapy used to treat bone and joint infections: an evidence-based algorithmic approach.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023 Jul-Dec;19(8):511-535. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2023.2255525. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37671793 Review.
-
The role of dalbavancin in the multi-disciplinary management of wound infections in orthopaedic surgery.J Chemother. 2018 May;30(3):131-139. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2017.1404277. Epub 2017 Nov 23. J Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29168673 Review.
-
Long-Acting Lipoglycopeptides for the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021 Oct;22(8):771-779. doi: 10.1089/sur.2020.413. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021. PMID: 33835882
-
Biofilm formation and antimicrobial susceptibility of staphylococci and enterococci from osteomyelitis associated with percutaneous orthopaedic implants.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017 Nov;105(8):2630-2640. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33803. Epub 2016 Oct 25. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27779811
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial potency, prevention ability, and killing efficacy of daptomycin-loaded versus vancomycin-loaded β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1029261. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1029261. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36406460 Free PMC article.
-
Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis: A Narrative Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;12(10):1485. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12101485. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus induces mitophagy via the HDAC11/IL10 pathway to sustain intracellular survival.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 4;23(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06161-7. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39905391 Free PMC article.
-
Local delivery of linezolid in the treatment of complex orthopedic bone and joint infections in patients with vancomycin allergy: a case series.J Bone Jt Infect. 2024 Mar 22;9(2):121-126. doi: 10.5194/jbji-9-121-2024. eCollection 2024. J Bone Jt Infect. 2024. PMID: 38779579 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic-Loaded Bioglass 45S5 for the Treatment and Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Orthopaedic Surgery: A Novel Strategy Against Antimicrobial Resistance.Pathogens. 2025 Aug 1;14(8):760. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14080760. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40872270 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

