Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Streptococcus suis Isolated from Diseased Pigs in Thailand, 2018-2020
- PMID: 35326873
- PMCID: PMC8944821
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030410
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Streptococcus suis Isolated from Diseased Pigs in Thailand, 2018-2020
Abstract
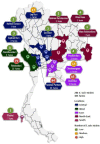
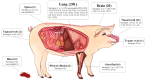
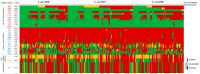
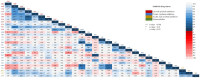
Streptococcus suis is a porcine and zoonotic pathogen that causes severe systemic infection in humans and pigs. The treatment of S. suis infection relies on antibiotics; however, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an urgent global problem, pushing research attention on the surveillance of antibiotic-resistant S. suis to the fore. This study investigated the antimicrobial susceptibility of 246 S. suis strains isolated from diseased pigs in Thailand from 2018-2020. The major sources of S. suis strains were lung and brain tissues. PCR-based serotyping demonstrated that the most abundant serotype was serotype 2 or ½, followed by serotypes 29, 8, 9, and 21. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report describing the distribution of AMR S. suis serotype 29 in diseased pigs. The antimicrobial susceptibility test was performed to determine the minimum inhibitory concentrations of 35 antimicrobial agents. The results showed that important antimicrobial agents for human use, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, daptomycin, ertapenem, meropenem, and vancomycin, were the most effective drugs. However, a slight decrease in the number of S. suis strains susceptible to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and vancomycin raised awareness of the AMR problem in the future. The data indicated a tendency of reduced efficacy of available veterinary medicines, including ampicillin, cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftiofur, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, florfenicol, gentamicin, penicillin, and tiamulin, for the treatment of S. suis infection, thus emphasizing the importance of the prudent use of antibiotics. The widespread of multidrug-resistant S. suis strains was identified in all serotypes and from different time periods and different regions of the country, confirming the emergence of the AMR problem in the diseased pig-isolated S. suis population.
Keywords: AMR; MDR; antimicrobial resistance; multidrug resistance; surveillance; zoonosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolated from diseased pigs, asymptomatic pigs, and human patients in Thailand.BMC Vet Res. 2019 Jan 3;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1732-5. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 30606175 Free PMC article.
-
Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolates from porcine diagnostic samples in Hungary, 2020-2023.Porcine Health Manag. 2025 Jan 8;11(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40813-024-00419-0. Porcine Health Manag. 2025. PMID: 39780272 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of multiple drug resistant Streptococcus suis in and around Guwahati, India.Vet World. 2017 May;10(5):556-561. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.556-561. Epub 2017 May 28. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28620262 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014 Jun;3(6):e45. doi: 10.1038/emi.2014.45. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 26038745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and prudent drug use for Streptococcus suis.Anim Health Res Rev. 2013 Jun;14(1):68-77. doi: 10.1017/S1466252313000029. Epub 2013 May 20. Anim Health Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 23683342 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Penicillin-Binding Proteins Alterations and β-Lactams Non-Susceptibility of Diseased Pig-Isolated Streptococcus suis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;12(1):158. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010158. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671359 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Streptococcus suis Isolates from the Czech Republic during 2018-2022.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 7;11(9):1214. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091214. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139993 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Macrolides Considering Evidence from Human and Veterinary Medicine.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 9;10(12):2438. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122438. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of integrative and conjugative elements carrying antibiotic resistance genes of Streptococcus suis isolated in China.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 22;13:1074844. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1074844. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36620002 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolated from pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Vet World. 2024 Feb;17(2):233-244. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.233-244. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 38595647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Segura M., Aragon V., Brockmeier S.L., Gebhart C., Greeff A., Kerdsin A., O’Dea M.A., Okura M., Saléry M., Schultsz C., et al. Update on Streptococcus suis research and prevention in the era of antimicrobial restriction: 4th International Workshop on S. suis. Pathogens. 2020;9:374. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050374. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

