Combination of Amphiphilic Cyclic Peptide [R4W4] and Levofloxacin against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
- PMID: 35326879
- PMCID: PMC8944500
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11030416
Combination of Amphiphilic Cyclic Peptide [R4W4] and Levofloxacin against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
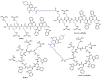
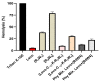
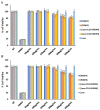
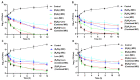
Bacterial resistance is a growing global concern necessitating the discovery and development of antibiotics effective against the drug-resistant bacterial strain. Previously, we reported a cyclic antimicrobial peptide [R4W4] containing arginine (R) and tryptophan (W) with a MIC of 2.67 µg/mL (1.95 µM) against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Herein, we investigated the cyclic peptides [R4W4] or linear (R4W4) and their conjugates (covalent or noncovalent) with levofloxacin (Levo) with the intent to improve their potency to target drug-resistant bacteria. The physical mixture of the Levo with the cyclic [R4W4] proved to be significantly effective against all strains of bacteria used in the study as compared to covalent conjugation. Furthermore, the checkerboard assay revealed the significant synergistic effect of the peptides against all studied strains except for the wild type S. aureus, in which the partial synergy was observed. The hemolysis assay revealed less cytotoxicity of the physical mixture of the Levo with [R4W4] (22%) as compared to [R4W4] alone (80%). The linear peptide (R4W4) and the cyclic [R4W4] demonstrated ~90% and 85% cell viability at 300 µg/mL in the triple-negative breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) and the normal kidney cells (HEK-293), respectively. Similar trends were also observed in the cell viability of Levo-conjugates on these cell lines. Furthermore, the time-kill kinetic study of the combination of [R4W4] and Levo demonstrate rapid killing action at 4 h for MRSA (ATCC BAA-1556) and 12 h for E. coli (ATCC BAA-2452), P. aeruginosa (ATCC BAA-1744), and K. pneumoniae (ATCC BAA-1705). These results provide the effectiveness of a combination of Levo with cyclic [R4W4] peptide, which may provide an opportunity to solve the intriguing puzzle of treating bacterial resistance.
Keywords: antibacterial resistance; checkerboard assay; combination therapy; cyclic antimicrobial peptides; drug-resistant bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activities of amphiphilic cyclic cell-penetrating peptides against multidrug-resistant pathogens.Mol Pharm. 2014 Oct 6;11(10):3528-36. doi: 10.1021/mp5003027. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25157458 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin and [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin-Q Conjugates.Molecules. 2017 Jun 8;22(6):957. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060957. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28594345 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiphilic cyclic peptide [W4KR5]-Antibiotics combinations as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 May 5;235:114278. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114278. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35339840
-
Cyclic Peptide [R4W4] in Improving the Ability of First-Line Antibiotics to Inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis Inside in vitro Human Granulomas.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 13;11:1677. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01677. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973740 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of ceftaroline against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae: a review of published studies and the AWARE Surveillance Program (2008-2010).Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Sep;55 Suppl 3:S206-14. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis563. Clin Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22903953 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Study of Antimicrobial Effectiveness of Cyclic Amphipathic Peptide [R4W4] against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 13;13(6):555. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060555. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927221 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Effects of Cyclic Peptide [R4W4] When Added Alongside Azithromycin and Rifampicin against Mycobacterium avium Infection.Pathogens. 2023 Aug 18;12(8):1057. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12081057. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37624017 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Temporin-SHa Retro Analogs with Lysine Addition/Substitution and Antibiotic Conjugation to Enhance Antibacterial, Antifungal, and Anticancer Activities.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 13;13(12):1213. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121213. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766603 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of cyclic peptide [R4W4] in combination with first-line therapy on the survival of Mycobacterium avium.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 16;15:1547376. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1547376. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40308965 Free PMC article.
-
The antimicrobial peptide Esc(1-21)-1c increases susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to conventional antibiotics by decreasing the expression of the MexAB-OprM efflux pump.Front Chem. 2023 Oct 24;11:1271153. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1271153. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37942400 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

